UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C.
FORM 10-Q
QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF
THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
| | |
For the quarterly period ended | September 29, 2018 | Commission file number 1–6770 |

MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
| |
Delaware | 25-0790410 |
(State or other jurisdiction | (I.R.S. Employer |
of incorporation or organization) | Identification No.) |
|
| |
8285 Tournament Drive, Suite 150 | |
Memphis, Tennessee | 38125 |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
(901) 753-3200
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
| |
Large accelerated filer ☒ | Accelerated filer ☐ |
Non-accelerated filer ☐ | Smaller reporting company ☐ |
| Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
Yes ☐ No ☒
The number of shares of the Registrant’s common stock outstanding as of October 19, 2018 was 57,669,954.
MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
FORM 10-Q
For the Quarterly Period Ended September 29, 2018
As used in this report, the terms “Company,” “Mueller,” and “Registrant” mean Mueller Industries, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries taken as a whole, unless the context indicates otherwise.
INDEX
PART I. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Item 1. Financial Statements
MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(Unaudited)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands, except per share data) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 (1) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 (1) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 645,958 |
| | $ | 550,363 |
| | $ | 1,948,791 |
| | $ | 1,742,549 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 566,956 |
| | 471,262 |
| | 1,676,446 |
| | 1,484,000 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 10,619 |
| | 8,266 |
| | 29,081 |
| | 25,216 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 38,889 |
| | 33,214 |
| | 112,077 |
| | 104,676 |
|
Asset impairments | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 411 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (2,691 | ) | | 140 |
| | (334 | ) | | (1,491 | ) |
Insurance recovery | | (1,486 | ) | | — |
| | (1,486 | ) | | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | 33,671 |
| | 37,481 |
| | 133,007 |
| | 129,737 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | (6,746 | ) | | (5,237 | ) | | (18,728 | ) | | (14,210 | ) |
Other income (expense), net | | 411 |
| | (380 | ) | | 1,557 |
| | 556 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | 27,336 |
| | 31,864 |
| | 115,836 |
| | 116,083 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Income tax expense | | (3,373 | ) | | (8,716 | ) | | (23,179 | ) | | (33,295 | ) |
Loss from unconsolidated affiliates, net of foreign tax | | (3,100 | ) | | (394 | ) | | (13,568 | ) | | (1,746 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Consolidated net income | | 20,863 |
| | 22,754 |
| | 79,089 |
| | 81,042 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | (571 | ) | | (496 | ) | | (1,487 | ) | | (1,164 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net income attributable to Mueller Industries, Inc. | | $ | 20,292 |
| | $ | 22,258 |
| | $ | 77,602 |
| | $ | 79,878 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Weighted average shares for basic earnings per share | | 56,877 |
| | 56,987 |
| | 56,858 |
| | 56,891 |
|
Effect of dilutive stock-based awards | | 540 |
| | 456 |
| | 524 |
| | 542 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Adjusted weighted average shares for diluted earnings per share | | 57,417 |
| | 57,443 |
| | 57,382 |
| | 57,433 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings per share | | $ | 0.36 |
| | $ | 0.39 |
| | $ | 1.36 |
| | $ | 1.40 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Diluted earnings per share | | $ | 0.35 |
| | $ | 0.39 |
| | $ | 1.35 |
| | $ | 1.39 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Dividends per share | | $ | 0.10 |
| | $ | 0.10 |
| | $ | 0.30 |
| | $ | 8.30 |
|
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
(1) The Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income for the quarter and nine months ended September 30, 2017 have been adjusted to reflect the adoption of ASU 2017-07, Compensation - Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Improving the Presentation of Net Periodic Pension Cost and Net Periodic Postretirement Benefit Cost. The components of net periodic benefit cost (income) other than the service cost component are included in other income (expense), net in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income. Refer to Note 1 for further discussion.
MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(Unaudited)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Consolidated net income | | $ | 20,863 |
| | $ | 22,754 |
| | $ | 79,089 |
| | $ | 81,042 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
|
Foreign currency translation | | 1,111 |
| | 7,154 |
| | (5,534 | ) | | 15,270 |
|
Net change with respect to derivative instruments and hedging activities, net of tax of $(33), $23, $243, and $(162) | | 131 |
| | (132 | ) | | (896 | ) | | 185 |
|
Net change in pension and postretirement obligation adjustments, net of tax of $(79), $102, $(221), and $285 | | 270 |
| | (207 | ) | | 769 |
| | (572 | ) |
Attributable to unconsolidated affiliates, net of tax of $2,005, $415, $2,086, and $614 | | (6,907 | ) | | (735 | ) | | (7,187 | ) | | (1,086 | ) |
Other, net | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (380 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total other comprehensive (loss) income, net | | (5,395 | ) | | 6,080 |
| | (12,848 | ) | | 13,417 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Consolidated comprehensive income | | 15,468 |
| | 28,834 |
| | 66,241 |
| | 94,459 |
|
Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | (34 | ) | | (499 | ) | | (1,097 | ) | | (2,002 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income attributable to Mueller Industries, Inc. | | $ | 15,434 |
| | $ | 28,335 |
| | $ | 65,144 |
| | $ | 92,457 |
|
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Unaudited) |
| | | | | | | | |
(In thousands, except share data) | | September 29,
2018 | | December 30,
2017 |
Assets | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 104,735 |
| | $ | 120,269 |
|
Accounts receivable, less allowance for doubtful accounts of $795 in 2018 and $980 in 2017 | | 308,231 |
| | 244,795 |
|
Inventories | | 313,396 |
| | 327,901 |
|
Other current assets | | 34,842 |
| | 46,150 |
|
| | | | |
Total current assets | | 761,204 |
| | 739,115 |
|
| | | | |
Property, plant, and equipment, net | | 360,655 |
| | 304,321 |
|
Goodwill, net | | 150,407 |
| | 130,293 |
|
Intangible assets, net | | 64,786 |
| | 42,008 |
|
Investments in unconsolidated affiliates | | 58,054 |
| | 80,286 |
|
Other assets | | 26,637 |
| | 24,150 |
|
| | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 1,421,743 |
| | $ | 1,320,173 |
|
| | | | |
Liabilities | | |
| | |
|
Current liabilities: | | |
| | |
|
Current portion of debt | | $ | 9,254 |
| | $ | 16,480 |
|
Accounts payable | | 121,412 |
| | 102,503 |
|
Accrued wages and other employee costs | | 37,703 |
| | 33,546 |
|
Other current liabilities | | 75,914 |
| | 89,723 |
|
| | | | |
Total current liabilities | | 244,283 |
| | 242,252 |
|
| | | | |
Long-term debt, less current portion | | 510,032 |
| | 448,592 |
|
Pension liabilities | | 9,941 |
| | 11,606 |
|
Postretirement benefits other than pensions | | 16,903 |
| | 17,107 |
|
Environmental reserves | | 21,339 |
| | 23,699 |
|
Deferred income taxes | | 17,299 |
| | 19,403 |
|
Other noncurrent liabilities | | 18,538 |
| | 21,486 |
|
| | | | |
Total liabilities | | 838,335 |
| | 784,145 |
|
| | | | |
Equity | | |
| | |
|
Mueller Industries, Inc. stockholders' equity: | | |
| | |
|
Preferred stock - $1.00 par value; shares authorized 5,000,000; none outstanding | | — |
| | — |
|
Common stock - $.01 par value; shares authorized 100,000,000; issued 80,183,004; outstanding 57,840,053 in 2018 and 57,809,509 in 2017 | | 802 |
| | 802 |
|
Additional paid-in capital | | 274,767 |
| | 274,585 |
|
Retained earnings | | 803,627 |
| | 743,503 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | (62,957 | ) | | (51,056 | ) |
Treasury common stock, at cost | | (447,253 | ) | | (445,723 | ) |
| | | | |
Total Mueller Industries, Inc. stockholders' equity | | 568,986 |
| | 522,111 |
|
Noncontrolling interests | | 14,422 |
| | 13,917 |
|
| | | | |
Total equity | | 583,408 |
| | 536,028 |
|
| | | | |
Commitments and contingencies | | — |
| | — |
|
Total liabilities and equity | | $ | 1,421,743 |
| | $ | 1,320,173 |
|
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Unaudited) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 (1) |
| | | | |
Cash flows from operating activities | | | | |
Consolidated net income | | $ | 79,089 |
| | $ | 81,042 |
|
Reconciliation of consolidated net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | |
| | |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 29,320 |
| | 25,439 |
|
Stock-based compensation expense | | 5,953 |
| | 5,555 |
|
Loss from unconsolidated affiliates | | 13,568 |
| | 1,746 |
|
Gain on sale of business | | — |
| | (1,491 | ) |
Gain on disposals of properties | | (247 | ) | | (26 | ) |
Gain on sales of securities | | — |
| | (611 | ) |
Impairment charge | | — |
| | 411 |
|
Insurance recovery | | (1,486 | ) | | — |
|
Deferred income taxes | | (1,502 | ) | | 624 |
|
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of businesses acquired and sold: | | |
| | |
|
Receivables | | (42,201 | ) | | (33,359 | ) |
Inventories | | 48,716 |
| | (40,920 | ) |
Other assets | | 11,250 |
| | (3,372 | ) |
Current liabilities | | (7,947 | ) | | 20,967 |
|
Other liabilities | | (13,862 | ) | | (1,498 | ) |
Other, net | | 1,864 |
| | (965 | ) |
| | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 122,515 |
| | 53,542 |
|
| | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities | | |
| | |
|
Capital expenditures | | (16,685 | ) | | (17,297 | ) |
Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | | (167,677 | ) | | (18,396 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of business, net of cash sold | | — |
| | 17,483 |
|
Investments in unconsolidated affiliates | | (609 | ) | | (3,317 | ) |
Proceeds from sales of assets | | 18,693 |
| | 11,732 |
|
Proceeds from sales of securities | | — |
| | 1,787 |
|
| | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | (166,278 | ) | | (8,008 | ) |
| | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities | | |
| | |
|
Dividends paid to stockholders of Mueller Industries, Inc. | | (17,051 | ) | | (191,241 | ) |
Dividends paid to noncontrolling interests | | (592 | ) | | (2,909 | ) |
Repurchase of common stock | | (6,575 | ) | | — |
|
Issuance of long-term debt | | 194,131 |
| | — |
|
Repayments of long-term debt | | (139,518 | ) | | (100,917 | ) |
Repayment of debt by consolidated joint ventures, net | | (2,978 | ) | | (3,451 | ) |
Net cash used to settle stock-based awards | | (726 | ) | | (1,644 | ) |
| | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | 26,691 |
| | (300,162 | ) |
| | | | |
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | | (442 | ) | | 4,466 |
|
| | | | |
Decrease in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | | (17,514 | ) | | (250,162 | ) |
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at the beginning of the period | | 126,563 |
| | 360,469 |
|
| | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at the end of the period | | $ | 109,049 |
| | $ | 110,307 |
|
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
(1) The Condensed Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 has been adjusted to reflect the adoption of ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. The Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows reflects the changes during the periods in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash. Therefore, restricted cash activity is included with cash when reconciling the beginning-of-period and end-of-period total amounts shown. Refer to Note 1 for further discussion.
MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unaudited)
General
Certain information and footnote disclosures normally included in annual financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (U.S. GAAP) have been condensed or omitted. Results of operations for the interim periods presented are not necessarily indicative of results which may be expected for any other interim period or for the year as a whole. This Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q should be read in conjunction with the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the annual financial statements incorporated therein.
The accompanying unaudited interim financial statements include all normal recurring adjustments which are, in the opinion of management, necessary for a fair presentation of the results for the interim periods presented herein.
Certain prior year balances have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation. Such reclassifications primarily relate to the adoptions of Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2017-07 and 2016-18 as further described in “Note 1 - Recent Accounting Standards.”
Note 1 – Recent Accounting Standards
Adopted
In February 2018, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued ASU No. 2018-02, Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (AOCI). The ASU permits entities to reclassify tax effects stranded in AOCI as a result of tax reform to retained earnings. The guidance is effective for the Company in interim and annual periods beginning in 2019. Early adoption is permitted and can be applied retrospectively or in the period of adoption. The Company early adopted the ASU during the first quarter of 2018, which resulted in a net reclassification of $556 thousand from AOCI to retained earnings during the quarter.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-07, Compensation - Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Improving the Presentation of Net Periodic Pension Cost and Net Periodic Postretirement Benefit Cost. The ASU requires employers that sponsor defined benefit pension and/or other postretirement benefit plans to present the service cost component of net periodic benefit cost in the same income statement line item(s) as other employee compensation costs arising from services rendered during the period and other components of net periodic benefits cost separately from the line item(s) that includes the service cost and outside of any subtotal of operating income. The Company adopted the ASU during the first quarter of 2018 using a retrospective approach for each period presented, and elected to use the practical expedient that allows the Company to use the amounts previously presented in its Benefit Plans disclosure as the estimation basis for applying the retrospective presentation requirements. Prior to the adoption of the ASU, net periodic benefit cost (income) was reported within selling, general, and administrative expense in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income. The prior periods have been revised to conform to the current period presentation, resulting in the reclassification of $78 thousand and $232 thousand of net periodic benefit income from operating income to other income (expense), net for the quarter and nine months ended September 30, 2017, respectively.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business. The ASU provides guidance to assist entities in evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of assets or businesses. The updated guidance requires prospective adoption. Early adoption is permitted. The Company early adopted the ASU during the first quarter of 2018 and the adoption had no impact on its Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
In December 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-20, Technical Corrections and Improvements to Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The ASU provides correction or improvement to the guidance previously issued in Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. Under the ASU, an entity will recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers at an amount that reflects the consideration that it expects to receive in exchange for the goods or services. It also requires more detailed disclosures to enable users of financial statements to understand the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers. The ASU requires revenue to be recognized over time (i.e., throughout the production process) rather than at a point in time (generally upon shipment to the customer) if performance does not create an asset with an alternative use to the entity and the entity has an enforceable right to payment for performance completed to date.
The Company generates revenue through the manufacture and sale of copper tube and fittings; line sets; brass and copper alloy rod, bar, and shapes; aluminum impact extrusions; plastic fittings and valves; refrigeration valves and fittings; fabricated tubular products; and steel nipples. The Company also resells imported brass and plastic plumbing valves, malleable iron fittings, faucets, and plumbing specialty products.
Given the nature of the Company’s business and product offerings, sales transactions with customers are generally comprised of a single performance obligation that involves delivery of the products identified in the contracts with customers. Performance obligations are generally satisfied at the point in time of shipment and payment is generally due within sixty days. Variable consideration is estimated for future rebates on certain product lines and product returns. The Company records variable consideration as an adjustment to the transaction price in the period it is incurred. Since variable consideration is settled within a short period of time, the time value of money is not significant.
The Company also evaluated specific contract terms, primarily within the Industrial Metals and Climate segments, related to the production of customized products and payment rights and determined that there are no significant changes to the timing or nature of revenue recognition under the ASU. As part of the overall evaluation of the standard, the Company has assessed and implemented necessary changes to its accounting policies, practices, and internal controls over financial reporting to support the standard.
The Company adopted the ASU during the first quarter of 2018 using the modified retrospective method for all contracts with customers. The adoption did not result in a significant impact on opening retained earnings. Revenue for prior periods have not been adjusted and continue to be reported under Revenue Recognition (Topic 605). No significant judgments were made in the application of the guidance in ASC 606 and there were no material contract assets, contract liabilities, or deferred contract costs as of September 29, 2018.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. The ASU requires entities to report the changes in the total of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents in the statement of cash flows. As a result, entities will no longer present transfers between cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents in the statement of cash flows. The Company adopted the ASU during the first quarter of 2018 using a retrospective approach for each period presented. Prior to the adoption of the ASU, the Company presented the change in restricted cash balances separately as a cash flow from investing activity. Upon adoption, the Company included restricted cash in each of the balances of the cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at the beginning and end of periods in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. The prior period has been revised to conform to the current period presentation, and as a result, net cash flows for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 increased by $4.0 million. A reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash as of September 29, 2018 and December 30, 2017 is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
(In thousands) | | September 29,
2018 | | December 30,
2017 |
| | | | |
Cash & cash equivalents | | $ | 104,735 |
| | $ | 120,269 |
|
Restricted cash included within other current assets | | 4,206 |
| | 6,189 |
|
Restricted cash included within other assets | | 108 |
| | 105 |
|
| | | | |
Total cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | | $ | 109,049 |
| | $ | 126,563 |
|
Amounts included in restricted cash relate to required deposits in brokerage accounts that facilitate the Company’s hedging activities as well as imprest funds for the Company’s self-insured workers’ compensation program.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory. The ASU requires companies to account for the income tax effects of intercompany transfers of assets other than inventory when the transfer occurs. Companies will still be required to defer the income tax effects of intercompany inventory transactions in an exception to the income tax accounting guidance. The Company adopted the ASU during the first quarter of 2018 and the adoption had no impact on its Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
Issued
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-14, Compensation - Retirement Benefits - Defined Benefit Plans - General (Subtopic 715-20): Disclosure Framework - Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Defined Benefit Plans. For employers that sponsor defined benefit pension and/or other postretirement benefit plans, the ASU eliminates requirements for certain
disclosures that are no longer considered cost beneficial, requires new disclosures related to the weighted-average interest crediting rate for cash balance plans and explanations for significant gains and losses related to changes in benefit obligations, and clarifies the requirements for entities that provide aggregate disclosures for two or more plans. The ASU will be effective for the annual period beginning in 2020. The updated guidance requires retrospective adoption, and early adoption is permitted. The Company does not expect the adoption of the ASU to have a material impact on its Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework - Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement. The ASU eliminates requirements to disclose the amount and reasons for transfers between level 1 and level 2 of the fair value hierarchy, but requires public companies to disclose changes in unrealized gains and losses for the period included in other comprehensive income (OCI) for recurring level 3 fair value measurements or instruments held at the end of the reporting period and the range and weighted average used to develop significant unobservable inputs for level 3 fair value measurements. The ASU will be effective for interim and annual periods beginning in 2020. An entity is permitted to early adopt either the entire standard or only the provisions that eliminate or modify requirements, and can elect to early adopt in interim periods. The guidance on changes in unrealized gains and losses for the period included in OCI for recurring level 3 measurements, the range and weighted average of significant unobservable inputs used to develop level 3 fair value measurements, and the narrative description of measurement uncertainty is applied prospectively. All other amendments should be applied retrospectively. The Company does not expect the adoption of the ASU to have a material impact on its Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
In July 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-11, Leases (Topic 842): Targeted Improvements and ASU No. 2018-10, Codification Improvements to Topic 842, Leases. The ASUs provide entities with relief from the costs of implementation and clarify how to apply certain aspects of the new leasing standard, ASC 842. ASC 842 requires an entity to recognize a right-of-use asset and lease liability for all leases with terms of more than 12 months. Recognition, measurement and presentation of expenses will depend on classification as a financing or operating lease. The guidance also require certain quantitative and qualitative disclosures about leasing arrangements. The ASU will be effective for interim and annual periods beginning in 2019. Early adoption is permitted. ASC 842 requires a modified retrospective adoption, but ASU 2018-11 amends ASC 842 so that entities may elect not to recast their comparative periods in transition and allows entities to change their date of initial application to the beginning of the period of adoption. The future minimum lease payments under noncancelable operating leases were approximately $40.5 million as of December 30, 2017. The Company is still evaluating the effects that the provisions of the ASUs and the ASC will have on its Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
Note 2 – Earnings per Common Share
Basic per share amounts have been computed based on the average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted per share amounts reflect the increase in average common shares outstanding that would result from the assumed exercise of outstanding stock options and vesting of restricted stock awards, computed using the treasury stock method. Approximately 79 thousand and 52 thousand stock-based awards were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share for the quarters ended September 29, 2018 and September 30, 2017, respectively, because they were antidilutive.
Note 3 – Acquisitions and Dispositions
Acquisitions
ATCO
On July 2, 2018, the Company entered into a stock purchase agreement pursuant to which the Company acquired all of the outstanding capital stock of ATCO Rubber Products, Inc. (ATCO) for approximately $156.7 million, net of working capital adjustments. The total purchase price consisted of $151.4 million in cash at closing and a contingent consideration arrangement which requires the Company to pay the former owner up to $12.0 million based on EBITDA growth of the acquired business. ATCO is an industry leader in the manufacturing and distribution of insulated HVAC flexible duct systems and will support the Company’s strategy to grow its Climate Products businesses to become a more valuable resource to its HVAC customers. The acquired business is reported in the Company’s Climate segment.
The fair value of the assets acquired totaled $139.2 million, consisting primarily of property, plant, and equipment of $83.2 million, inventories of $33.1 million, accounts receivable of $21.8 million, other current assets of $0.8 million, and other assets of $0.3 million. The fair value of the liabilities assumed totaled $19.8 million, consisting primarily of accounts payable of $8.1 million, other current liabilities of $9.6 million, and other liabilities of $2.1 million. Of the remaining purchase price, $15.9 million was allocated to tax-deductible goodwill and $21.4 million was allocated to intangible assets, including technology, customer relationships, trade names, and supply contracts. The purchase price allocation is provisional as of September 29, 2018 and subject
to change upon completion of the final valuation of the long-lived assets, working capital, and contingent consideration during the measurement period.
ATCO had revenues of approximately $166.0 million in its fiscal year ending December 31, 2017.
The following table presents condensed pro forma consolidated results of operations as if the ATCO acquisition has occurred at the beginning of the periods presented. The pro forma information does not purport to be indicative of the results that would have been obtained if the operations had actually been combined during the periods presented, and is not necessarily indicative of operating results to be expected in future periods. The most significant pro forma adjustments to the historical results of operations relate to the application of purchase accounting and financing structure.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands, except per share data) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 2,036,367 |
| | $ | 1,868,677 |
|
Net income | | 84,823 |
| | 82,523 |
|
| | | | |
Basic earnings per share | | $ | 1.49 |
| | $ | 1.45 |
|
Diluted earnings per share | | 1.48 |
| | 1.44 |
|
Die-Mold
On March 31, 2018, the Company entered into a share purchase agreement pursuant to which the Company acquired all of the outstanding shares of Die-Mold Tool Limited (Die-Mold) for approximately $13.6 million, net of working capital adjustments. The total purchase price consisted of $12.4 million in cash at closing and a contingent consideration arrangement which requires the Company to pay the former owner up to $2.3 million based on EBITDA growth of the acquired business. Die-Mold, based out of Ontario, Canada, is a manufacturer of plastic PEX and other plumbing-related fittings and an integrated designer and manufacturer of plastic injection tooling. The business complements the Company’s existing businesses within the Piping Systems segment.
The fair value of the assets acquired totaled $7.0 million, consisting primarily of property, plant, and equipment of $3.3 million, inventories of $1.8 million, and accounts receivable of $1.7 million. The fair value of the liabilities assumed totaled $0.9 million, consisting primarily of accounts payable of $0.7 million and other current liabilities of $0.2 million. Of the remaining purchase price, $7.5 million was allocated to non-deductible goodwill and intangible assets. The purchase price allocation is provisional as of September 29, 2018 and subject to change upon completion of the final valuation of the long-lived assets and contingent consideration during the measurement period.
Heatlink Group
On May 31, 2017, the Company entered into a share purchase agreement pursuant to which the Company acquired all of the outstanding shares of Pexcor Manufacturing Company Inc. and Heatlink Group Inc. (collectively, Heatlink Group) for approximately $17.2 million, net of working capital adjustments. The total purchase price consisted of $16.3 million in cash at closing and a contingent consideration arrangement which requires the Company to pay the former owners up to $2.2 million based on the EBITDA growth of the acquired business. Heatlink Group, based out of Calgary, Alberta, Canada, produces and sells a complete line of products for PEX plumbing and radiant systems. The business complements the Company’s existing businesses within the Piping Systems segment.
The fair value of the assets acquired totaled $9.9 million, consisting primarily of inventories of $4.6 million, accounts receivable of $2.8 million, property, plant, and equipment of $2.0 million, and other current assets of $0.5 million. The fair value of the liabilities assumed totaled $6.0 million, consisting primarily of accounts payable of $3.6 million, other current liabilities of $0.5 million, and deferred taxes of $1.9 million. Of the remaining purchase price, $13.3 million was allocated to non-deductible goodwill and intangible assets. The valuation of the business has been finalized. Changes to the purchase price allocation from the amounts presented in the Company’s 2017 Annual Report on Form 10-K included the valuation of the contingent consideration of $0.9 million and the recognition of a deferred tax liability of $1.9 million that resulted from a basis difference in the long-lived assets acquired. These changes resulted in an increase to goodwill.
Disposition
Mueller-Xingrong
On June 21, 2017, the Company entered into a definitive equity transfer agreement with Jiangsu Xingrong Hi-Tech Co. Ltd. and Jiangsu Baiyang Industries Co. Ltd. (Baiyang), together, the minority partners in Mueller-Xingrong (the Company’s Chinese joint venture), pursuant to which the Company sold its 50.5 percent equity interest in Mueller-Xingrong to Baiyang for approximately $18.3 million. Mueller-Xingrong manufactures engineered copper tube primarily for air-conditioning applications in China and was included in the Piping Systems segment. Mueller-Xingrong reported net sales of $67.3 million and net losses of $9 thousand in 2017. The carrying value of the assets disposed totaled $56.8 million, consisting primarily of accounts receivable, inventories, and long-lived assets. The carrying value of the liabilities disposed (consisting primarily of current debt and accounts payable), noncontrolling interest, and amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) totaled $36.2 million. Since the disposal constituted a complete liquidation of the Company’s investment in a foreign entity, the Company removed from AOCI and recognized a cumulative translation gain of $3.8 million. As a result of the disposal, the Company recognized a net gain on the sale of this business of $1.5 million in the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements for the nine months ended September 30, 2017.
Note 4 – Segment Information
Each of the Company’s reportable segments is composed of certain operating segments that are aggregated primarily by the nature of products offered as follows:
Piping Systems
Piping Systems is composed of the following operating segments: Domestic Piping Systems Group, Great Lakes Copper, Heatlink Group, Die-Mold, European Operations, Trading Group, and Jungwoo-Mueller (the Company’s South Korean joint venture). The Domestic Piping Systems Group manufactures copper tube, fittings, and line sets. These products are manufactured in the U.S., sold in the U.S., and exported to markets worldwide. Outside the U.S., Great Lakes Copper manufactures copper tube and line sets in Canada and sells the products primarily in the U.S. and Canada, Heatlink Group produces a complete line of products for PEX plumbing and radiant systems in Canada and sells these products in Canada and the U.S., Die-Mold manufactures PEX and other plumbing-related fittings and plastic injection tooling in Canada and sells these products in Canada and the U.S., and the European Operations manufacture copper tube in the U.K. which is sold primarily in Europe. The Trading Group manufactures pipe nipples and imports and resells brass and plastic plumbing valves, malleable iron fittings, faucets, and plumbing specialty products in the U.S. and Mexico. Jungwoo-Mueller manufactures copper-based joining products that are sold worldwide. The Piping Systems segment’s products are sold primarily to plumbing, refrigeration, and air-conditioning wholesalers, hardware wholesalers and co-ops, building product retailers, and air-conditioning original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
Industrial Metals
Industrial Metals is composed of the following operating segments: Brass Rod & Copper Bar Products, Impacts & Micro Gauge, and Brass Value-Added Products. These businesses manufacture brass rod, impact extrusions, and forgings, as well as a wide variety of end products including plumbing brass, automotive components, valves, fittings, and gas assemblies. These products are manufactured in the U.S. and sold primarily to OEMs in the U.S., many of which are in the industrial, transportation, construction, heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning, plumbing, refrigeration, and energy markets.
Climate
Climate is composed of the following operating segments: Refrigeration Products, Fabricated Tube Products, Westermeyer, Turbotec, and ATCO. These domestic businesses manufacture and fabricate valves, assemblies, high pressure components, coaxial heat exchangers, and insulated HVAC flexible duct systems primarily for the heating, ventilation, air-conditioning, and refrigeration markets in the U.S.
Summarized segment information is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Corporate and Eliminations | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 410,525 |
| | $ | 158,709 |
| | $ | 81,619 |
| | $ | (4,895 | ) | | $ | 645,958 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 363,174 |
| | 141,435 |
| | 66,832 |
| | (4,485 | ) | | 566,956 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 5,946 |
| | 1,864 |
| | 2,123 |
| | 686 |
| | 10,619 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 17,387 |
| | 3,086 |
| | 6,890 |
| | 11,526 |
| | 38,889 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (1,390 | ) | | (1,301 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,691 | ) |
Insurance recovery | | — |
| | (1,486 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,486 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | 25,408 |
| | 15,111 |
| | 5,774 |
| | (12,622 | ) | | 33,671 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | (6,746 | ) |
Other income (expense), net | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 411 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | $ | 27,336 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Corporate and Eliminations | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 384,078 |
| | $ | 147,578 |
| | $ | 32,488 |
| | $ | (13,781 | ) | | $ | 550,363 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 340,191 |
| | 120,021 |
| | 24,111 |
| | (13,061 | ) | | 471,262 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 5,290 |
| | 1,845 |
| | 636 |
| | 495 |
| | 8,266 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 17,516 |
| | 3,014 |
| | 2,312 |
| | 10,372 |
| | 33,214 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | 140 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 140 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | 20,941 |
| | 22,698 |
| | 5,429 |
| | (11,587 | ) | | 37,481 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | (5,237 | ) |
Other loss, net | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | (380 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | $ | 31,864 |
|
Segment information (continued):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Corporate and Eliminations | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 1,294,672 |
| | $ | 511,932 |
| | $ | 156,854 |
| | $ | (14,667 | ) | | $ | 1,948,791 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 1,120,890 |
| | 445,259 |
| | 124,806 |
| | (14,509 | ) | | 1,676,446 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 17,568 |
| | 5,715 |
| | 3,371 |
| | 2,427 |
| | 29,081 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 57,931 |
| | 9,908 |
| | 12,009 |
| | 32,229 |
| | 112,077 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (2,093 | ) | | (1,301 | ) | | — |
| | 3,060 |
| | (334 | ) |
Insurance recovery | | — |
| | (1,486 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,486 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | 100,376 |
| | 53,837 |
| | 16,668 |
| | (37,874 | ) | | 133,007 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | (18,728 | ) |
Other income, net | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 1,557 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | $ | 115,836 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Corporate and Eliminations | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 1,205,697 |
| | $ | 451,919 |
| | $ | 103,403 |
| | $ | (18,470 | ) | | $ | 1,742,549 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 1,049,098 |
| | 377,036 |
| | 77,124 |
| | (19,258 | ) | | 1,484,000 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 16,223 |
| | 5,647 |
| | 1,880 |
| | 1,466 |
| | 25,216 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 55,133 |
| | 9,802 |
| | 7,244 |
| | 32,497 |
| | 104,676 |
|
Asset impairments | | 411 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 411 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (1,491 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,491 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | 86,323 |
| | 59,434 |
| | 17,155 |
| | (33,175 | ) | | 129,737 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | (14,210 | ) |
Other income, net | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 556 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | $ | 116,083 |
|
The following tables represent a disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers, along with the reportable segment for each category:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Total |
| | | | | | | | |
Tube and fittings | | $ | 340,269 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 340,269 |
|
Brass rod and forgings | | — |
| | 122,411 |
| | — |
| | 122,411 |
|
OEM components, tube & assemblies | | 7,618 |
| | 12,292 |
| | 35,555 |
| | 55,465 |
|
Valves and plumbing specialties | | 62,638 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 62,638 |
|
Other | | — |
| | 24,006 |
| | 46,064 |
| | 70,070 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 410,525 |
| | 158,709 |
| | 81,619 |
| | 650,853 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Intersegment sales | | | | | | | | (4,895 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | | | | | | | $ | 645,958 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Total |
| | | | | | | | |
Tube and fittings | | $ | 319,115 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 319,115 |
|
Brass rod and forgings | | — |
| | 112,592 |
| | — |
| | 112,592 |
|
OEM components, tube & assemblies | | 6,962 |
| | 13,051 |
| | 32,488 |
| | 52,501 |
|
Valves and plumbing specialties | | 58,001 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 58,001 |
|
Other | | — |
| | 21,935 |
| | — |
| | 21,935 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 384,078 |
| | 147,578 |
| | 32,488 |
| | 564,144 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Intersegment sales | | | | | | | | (13,781 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | | | | | | | $ | 550,363 |
|
Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers (continued):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Total |
| | | | | | | | |
Tube and fittings | | $ | 1,077,525 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 1,077,525 |
|
Brass rod and forgings | | — |
| | 394,880 |
| | — |
| | 394,880 |
|
OEM components, tube & assemblies | | 22,128 |
| | 41,956 |
| | 110,790 |
| | 174,874 |
|
Valves and plumbing specialties | | 195,019 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 195,019 |
|
Other | | — |
| | 75,096 |
| | 46,064 |
| | 121,160 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 1,294,672 |
| | 511,932 |
| | 156,854 |
| | 1,963,458 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Intersegment sales | | | | | | | | (14,667 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | | | | | | | $ | 1,948,791 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | Piping Systems | | Industrial Metals | | Climate | | Total |
| | | | | | | | |
Tube and fittings | | $ | 945,914 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 945,914 |
|
Brass rod and forgings | | — |
| | 346,555 |
| | — |
| | 346,555 |
|
OEM components, tube & assemblies | | 86,642 |
| | 39,153 |
| | 103,403 |
| | 229,198 |
|
Valves and plumbing specialties | | 173,141 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 173,141 |
|
Other | | — |
| | 66,211 |
| | — |
| | 66,211 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 1,205,697 |
| | 451,919 |
| | 103,403 |
| | 1,761,019 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Intersegment sales | | | | | | | | (18,470 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | | | | | | | $ | 1,742,549 |
|
Note 5 – Inventories
|
| | | | | | | | |
(In thousands) | | September 29,
2018 | | December 30,
2017 |
| | | | |
Raw materials and supplies | | $ | 87,605 |
| | $ | 108,397 |
|
Work-in-process | | 61,138 |
| | 46,158 |
|
Finished goods | | 171,725 |
| | 180,143 |
|
Valuation reserves | | (7,072 | ) | | (6,797 | ) |
| | | | |
Inventories | | $ | 313,396 |
| | $ | 327,901 |
|
Note 6 – Financial Instruments
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
The Company’s earnings and cash flows are subject to fluctuations due to changes in commodity prices, foreign currency exchange rates, and interest rates. The Company uses derivative instruments such as commodity futures contracts, foreign currency forward contracts, and interest rate swaps to manage these exposures.
All derivatives are recognized in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets at their fair value. On the date the derivative contract is entered into, it is either a) designated as a hedge of (i) a forecasted transaction or the variability of cash flow to be paid (cash flow hedge) or (ii) the fair value of a recognized asset or liability (fair value hedge), or b) not designated in a hedge accounting relationship, even though the derivative contract was executed to mitigate an economic exposure (economic hedge), as the Company does not enter into derivative contracts for trading purposes. Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is qualified, designated, and highly effective as a cash flow hedge are recorded in stockholders’ equity within AOCI, to the extent effective, until they are reclassified to earnings in the same period or periods during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is qualified, designated, and highly effective as a fair value hedge, along with the gain or loss on the hedged recognized asset or liability that is attributable to the hedged risk, are recorded in current earnings. Changes in the fair value of undesignated derivatives executed as economic hedges and the ineffective portion of designated derivatives are reported in current earnings.
The Company documents all relationships between derivative instruments and hedged items, as well as the risk-management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. This process includes linking all derivative instruments that are designated as fair value hedges to specific assets and liabilities in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets and linking cash flow hedges to specific forecasted transactions or variability of cash flow.
The Company also assesses, both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis, whether the designated derivative instruments that are used in hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows or fair values of hedged items. When a derivative instrument is determined not to be highly effective as a hedge or the underlying hedged transaction is no longer probable of occurring, hedge accounting is discontinued prospectively in accordance with the derecognition criteria for hedge accounting.
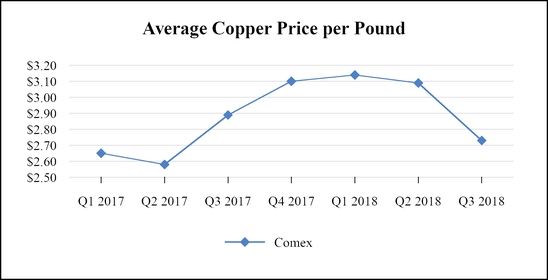
Commodity Futures Contracts
Copper and brass represent the largest component of the Company’s variable costs of production. The cost of these materials is subject to global market fluctuations caused by factors beyond the Company’s control. The Company occasionally enters into forward fixed-price arrangements with certain customers; the risk of these arrangements is generally managed with commodity futures contracts. These futures contracts have been designated as cash flow hedges.
At September 29, 2018, the Company held open futures contracts to purchase approximately $66.0 million of copper over the next 15 months related to fixed price sales orders. The fair value of those futures contracts was an $839 thousand net loss position, which was determined by obtaining quoted market prices (level 1 within the fair value hierarchy). In the next 12 months, the Company will reclassify into earnings realized gains or losses relating to cash flow hedges. At September 29, 2018, this amount was approximately $90 thousand of deferred net losses, net of tax.
The Company may also enter into futures contracts to protect the value of inventory against market fluctuations. At September 29, 2018, the Company held open futures contracts to sell approximately $4.5 million of copper over the next three months related to copper inventory. The fair value of those futures contracts was a $32 thousand net loss position, which was determined by obtaining quoted market prices (level 1 within the fair value hierarchy).
The Company presents its derivative assets and liabilities in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets on a net basis by counterparty. The following table summarizes the location and fair value of the derivative instruments and disaggregates the net derivative assets and liabilities into gross components on a contract-by-contract basis:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Asset Derivatives | | Liability Derivatives |
| | | | Fair Value | | | | Fair Value |
(In thousands) | | Balance Sheet Location | | September 29,
2018 | | December 30,
2017 | | Balance Sheet Location | | September 29,
2018 | | December 30,
2017 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts - gains | | Other current assets | | $ | 207 |
| | $ | 1,014 |
| | Other current liabilities | | $ | 880 |
| | $ | 55 |
|
Commodity contracts - losses | | Other current assets | | (127 | ) | | (5 | ) | | Other current liabilities | | (1,831 | ) | | (3,210 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total derivatives (1) | | | | $ | 80 |
| | $ | 1,009 |
| | | | $ | (951 | ) | | $ | (3,155 | ) |
(1) Does not include the impact of cash collateral provided to counterparties.
The following tables summarize the effects of derivative instruments on the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | Location | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
Fair value hedges: | | | | | | | | | | |
Gain on commodity contracts (qualifying) | | Cost of goods sold | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 391 |
| | $ | — |
|
Loss on hedged item - inventory | | Cost of goods sold | | — |
| | — |
| | (385 | ) | | — |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Undesignated derivatives: | | | | | | | | | | |
(Loss) gain on commodity contracts (nonqualifying) | | Cost of goods sold | | (2,848 | ) | | (3,083 | ) | | 5,579 |
| | (3,506 | ) |
The following tables summarize amounts recognized in and reclassified from AOCI during the period:
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Gain Recognized in AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax | | Classification Gains (Losses) | | Gain Reclassified from AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts | | $ | 305 |
| | Cost of goods sold | | $ | (180 | ) |
Other | | 6 |
| | Other | | — |
|
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 311 |
| | Total | | $ | (180 | ) |
Changes recognized in and reclassified from AOCI (continued):
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | (Loss) Gain Recognized in AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax | | Classification Gains (Losses) | | Loss Reclassified from AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts | | $ | (541 | ) | | Cost of goods sold | | $ | 237 |
|
Interest rate swap | | — |
| | Interest expense | | 149 |
|
Other | | 23 |
| | Other | | — |
|
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | (518 | ) | | Total | | $ | 386 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Loss Recognized in AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax | | Classification Gains (Losses) | | Gain Reclassified from AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts | | $ | (438 | ) | | Cost of goods sold | | $ | (455 | ) |
Other | | (3 | ) | | Other | | — |
|
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | (441 | ) | | Total | | $ | (455 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | (Loss) Gain Recognized in AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax | | Classification Gains (Losses) | | Loss Reclassified from AOCI (Effective Portion), Net of Tax |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts | | $ | (1,354 | ) | | Cost of goods sold | | $ | 913 |
|
Interest rate swap | | — |
| | Interest expense | | 447 |
|
Other | | 179 |
| | Other | | — |
|
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | (1,175 | ) | | Total | | $ | 1,360 |
|
The Company enters into futures and forward contracts that closely match the terms of the underlying transactions. As a result, the ineffective portion of the qualifying open hedge contracts through September 29, 2018 was not material to the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income.
The Company primarily enters into International Swaps and Derivatives Association master netting agreements with major financial institutions that permit the net settlement of amounts owed under their respective derivative contracts. Under these master netting agreements, net settlement generally permits the Company or the counterparty to determine the net amount payable for contracts due on the same date and in the same currency for similar types of derivative transactions. The master netting agreements generally also provide for net settlement of all outstanding contracts with a counterparty in the case of an event of default or a termination event. The Company does not offset fair value amounts for derivative instruments and fair value amounts recognized for the right to reclaim cash collateral. At September 29, 2018 and December 30, 2017, the Company had recorded restricted cash in other current assets of $3.4 million and $5.3 million, respectively, as collateral related to open derivative contracts under the master netting arrangements.
Long-Term Debt
The fair value of long-term debt at September 29, 2018 approximates the carrying value on that date. The estimated fair values were determined based on quoted market prices and the current rates offered for debt with similar terms and maturities. The fair value of long-term debt is classified as level 2 within the fair value hierarchy. This classification is defined as a fair value determined using market-based inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the liability, either directly or indirectly.
Note 7 – Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliates
Tecumseh
The Company owns a 50 percent interest in an unconsolidated affiliate that acquired Tecumseh Products Company LLC (Tecumseh). The Company also owns a 50 percent interest in a second unconsolidated affiliate that provides financing to Tecumseh. These investments are recorded using the equity method of accounting, as the Company can exercise significant influence but does not own a majority equity interest or otherwise control the respective entities. Under the equity method of accounting, these investments are stated at initial cost and are adjusted for subsequent additional investments and the Company’s proportionate share of earnings or losses and distributions.
The Company records its proportionate share of the investees’ income or loss, net of foreign taxes, one quarter in arrears as income (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates, net of foreign tax, in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and its proportionate share of the investees’ other comprehensive income (loss), net of income taxes, in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income. The U.S. tax effect of the Company’s proportionate share of Tecumseh’s income or loss is recorded in income tax expense in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income. In general, the equity investment in unconsolidated affiliates is equal to the current equity investment plus the investees’ net accumulated losses.
The following tables present summarized financial information derived from the Company’s equity method investees’ combined consolidated financial statements, which are prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
|
| | | | | | | | |
(In thousands) | | September 29,
2018 | | December 30,
2017 |
| | | | |
Current assets | | $ | 222,408 |
| | $ | 246,127 |
|
Noncurrent assets | | 112,547 |
| | 139,200 |
|
Current liabilities | | 163,931 |
| | 174,710 |
|
Noncurrent liabilities | | 60,112 |
| | 58,334 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 131,827 |
| | $ | 148,400 |
| | $ | 382,132 |
| | $ | 407,300 |
|
Gross profit | | 18,140 |
| | 21,500 |
| | 41,989 |
| | 56,700 |
|
Net loss | | (5,007 | ) | | (788 | ) | | (22,867 | ) | | (3,492 | ) |
The Company’s loss from unconsolidated affiliates, net of foreign tax, for the quarter ended September 29, 2018 included net losses of $2.5 million for Tecumseh.
The Company’s loss from unconsolidated affiliates, net of foreign tax, for the nine months ended September 29, 2018 included net losses of $15.4 million and charges of $3.0 million related to certain labor claim contingencies, offset by a gain of $7.0 million related to a settlement with the Brazilian Federal Revenue Agency for Tecumseh.
Bahrain
On December 30, 2015, the Company entered into a joint venture agreement with Cayan Ventures and Bahrain Mumtalakat Holding
Company to build a copper tube mill in Bahrain. The business will operate and brand its products under the Mueller Industries family of brands. The Company has invested approximately $4.5 million of cash to date and will be the technical and marketing lead in return for 40 percent ownership in the joint venture.
The Company’s loss from unconsolidated affiliates, net of foreign tax, for the quarter and nine months ended September 29, 2018 included net losses of $0.5 million and $2.1 million, respectively, for Bahrain.
Note 8 – Benefit Plans
The Company sponsors several qualified and nonqualified pension plans and other postretirement benefit plans for certain of its employees. The components of net periodic benefit cost (income) are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Pension benefits: | | | | | | | | |
Service cost | | $ | 22 |
| | $ | 35 |
| | $ | 66 |
| | $ | 106 |
|
Interest cost | | 1,478 |
| | 1,659 |
| | 4,436 |
| | 4,977 |
|
Expected return on plan assets | | (2,290 | ) | | (2,184 | ) | | (6,869 | ) | | (6,552 | ) |
Amortization of net loss | | 293 |
| | 536 |
| | 877 |
| | 1,608 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Net periodic benefit (income) cost | | $ | (497 | ) | | $ | 46 |
| | $ | (1,490 | ) | | $ | 139 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Other benefits: | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
|
Service cost | | $ | 59 |
| | $ | 54 |
| | $ | 175 |
| | $ | 163 |
|
Interest cost | | 147 |
| | 147 |
| | 441 |
| | 442 |
|
Amortization of prior service credit | | (226 | ) | | (225 | ) | | (677 | ) | | (676 | ) |
Amortization of net loss (gain) | | 14 |
| | (10 | ) | | 43 |
| | (30 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net periodic benefit income | | $ | (6 | ) | | $ | (34 | ) | | $ | (18 | ) | | $ | (101 | ) |
The components of net periodic benefit cost (income) other than the service cost component are included in other income (expense), net in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income.
Note 9 – Commitments and Contingencies
The Company is involved in certain litigation as a result of claims that arose in the ordinary course of business, which management believes will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. The Company may also realize the benefit of certain legal claims and litigation in the future; these gain contingencies are not recognized in the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
Environmental
Non-operating Properties
Southeast Kansas Sites
The Kansas Department of Health and Environment (KDHE) has contacted the Company regarding environmental contamination at three former smelter sites in Kansas (Altoona, East La Harpe, and Lanyon). The Company is not a successor to the companies that operated these smelter sites, but is exploring possible settlement with KDHE and other potentially responsible parties (PRP) in order to avoid litigation. Another PRP conducted a site investigation of the Altoona site under a consent decree with KDHE and submitted a removal site evaluation report recommending a remedy. The remedial design plan, which covers both on-site and certain off-site cleanup costs, was approved by the KDHE in 2016. At the East La Harpe site, the Company and two other PRPs conducted a site study evaluation under KDHE supervision and prepared a site cleanup plan approved by KDHE. In 2016, the
corporate parent of a third party that the Company understands may owe indemnification obligations to one of the other PRPs in connection with the East La Harpe site filed for protection under Chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code. KDHE has extended the deadline for the PRPs to develop a repository design plan to allow for wetlands permitting to take place. With respect to the Lanyon Site, in 2016, the Company received a general notice letter from the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) asserting that the Company is a PRP, which the Company has denied. The Company’s reserve for its proportionate share of the remediation costs associated with the Southeast Kansas sites is $5.6 million.
Shasta Area Mine Sites
Mining Remedial Recovery Company (MRRC), a wholly owned subsidiary, owns certain inactive mines in Shasta County, California. MRRC has continued a program, begun in the late 1980s, of implementing various remedial measures, including sealing mine portals with concrete plugs in portals that were discharging water. The sealing program achieved significant reductions in the metal load in discharges from these adits; however, additional reductions are required pursuant to an order issued by the California Regional Water Quality Control Board (QCB). In response to a 1996 QCB Order, MRRC completed a feasibility study in 1997 describing measures designed to mitigate the effects of acid rock drainage. In December 1998, the QCB modified the 1996 order extending MRRC’s time to comply with water quality standards. In September 2002, the QCB adopted a new order requiring MRRC to adopt Best Management Practices (BMP) to control discharges of acid mine drainage, and again extended the time to comply with water quality standards until September 2007. During that time, implementation of BMP further reduced impacts of acid rock drainage; however, full compliance has not been achieved. The QCB is presently renewing MRRC’s discharge permit and will concurrently issue a new order. It is expected that the new 10-year permit will include an order requiring continued implementation of BMP through 2029 to address residual discharges of acid rock drainage. The Company currently estimates that it will spend between approximately $12.8 million and $17.6 million for remediation at these sites over the next 30 years.
Lead Refinery Site
U.S.S. Lead Refinery, Inc. (Lead Refinery), a non-operating wholly owned subsidiary of MRRC, has conducted corrective action and interim remedial activities (collectively, Site Activities) at Lead Refinery’s East Chicago, Indiana site pursuant to the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act since December 1996. Although the Site Activities have been substantially concluded, Lead Refinery is required to perform monitoring and maintenance-related activities pursuant to a post-closure permit issued by the Indiana Department of Environmental Management effective as of March 2, 2013. Approximate costs to comply with the post-closure permit, including associated general and administrative costs, are estimated at between $1.8 million and $3.0 million over the next 19 years.
On April 9, 2009, pursuant to the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) added the Lead Refinery site and surrounding properties to the National Priorities List (NPL). On July 17, 2009, Lead Refinery received a written notice from the EPA indicating that it may be a PRP under CERCLA due to the release or threat of release of hazardous substances including lead into properties surrounding the Lead Refinery NPL site. The EPA identified two other PRPs in connection with that matter. In November 2012, the EPA adopted a remedy for the surrounding properties and in September 2014, the EPA announced that it had entered into a settlement with the two other PRPs whereby they will pay approximately $26.0 million to fund the cleanup of approximately 300 properties surrounding the Lead Refinery NPL site (zones 1 and 3 of operable unit 1) and perform certain remedial action tasks.
On November 8, 2016, the Company, its subsidiary Arava Natural Resources Company, Inc. (Arava), and Arava’s subsidiary MRRC each received general notice letters from the EPA asserting that they may be PRPs in connection with the Lead Refinery NPL site. The Company, Arava, and MRRC have denied liability for any remedial action and response costs associated with the Lead Refinery NPL site. In June 2017, the EPA requested that Lead Refinery conduct, and the Company fund, a remedial investigation and feasibility study of operable unit 2 of the Lead Refinery NPL site pursuant to a proposed administrative settlement agreement and order on consent. The Company and Lead Refinery entered into that agreement in September 2017. The Company has made a capital contribution to Lead Refinery to conduct the remedial investigation and feasibility study with respect to operable unit 2 and has provided financial assurance in the amount of $1.0 million. The EPA has also asserted its position that Mueller is a responsible party for the Lead Refinery NPL site, and accordingly is responsible for a share of remedial action and response costs at the site and in the adjacent residential area.
In January 2018, the EPA issued two unilateral administrative orders (UAOs) directing the Company, Lead Refinery, and four other PRPs to conduct soil and interior remediation of certain residences at the Lead Refinery NPL site (zones 2 and 3 of operable unit 1). The Company and Lead Refinery have reached agreement with the four other PRPs to implement these two UAOs, with the Company agreeing to pay, on an interim basis, (i) an estimated $4.5 million (subject to potential change through a future reallocation process) of the approximately $25.0 million the PRPs currently estimate it will cost to implement the UAOs, which estimate is subject to change, and (ii) $2.0 million relating to past costs incurred by other PRPs for work conducted at the site.
These amounts are included in the Company’s reserve for environmental liabilities as of December 30, 2017. The Company disputes that it was properly named in the UAOs, and has reserved its rights to petition the EPA for reimbursement of any costs incurred to comply with the UAOs upon the completion of the work required therein. In October 2017, a group of private plaintiffs sued the Company, Arava, MRRC, and Lead Refinery, along with other defendants, in a private tort action relating to the site; the Company, Arava, and MRRC were voluntarily dismissed from that litigation without prejudice in March 2018. A second civil action asserting similar claims was filed against the Company, Arava, MRRC, and Lead Refinery in September 2018. At this juncture, the Company is unable to determine the likelihood of a material adverse outcome or the amount or range of a potential loss in excess of the current reserve with respect to any remedial action or litigation relating to the Lead Refinery NPL site, either at Lead Refinery’s former operating site (operable unit 2) or the adjacent residential area (operable unit 1).
Bonita Peak Mining District
Following an August 2015 spill from the Gold King Mine into the Animas River near Silverton, Colorado, the EPA listed the Bonita Peak Mining District on the NPL. Said listing was finalized in September 2016. The Bonita Peak Mining District encompasses 48 mining sites within the Animas River watershed, including the Sunnyside Mine, the American Tunnel, and the Sunbank Group. On or about July 25, 2017, Washington Mining Company (Washington Mining) (a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary, Arava), received a general notice letter from the EPA stating that Washington Mining may be a PRP under CERCLA in connection with the Bonita Peak Mining District site and therefore responsible for the remediation of certain portions of the site, along with related costs incurred by the EPA. Shortly thereafter, the Company received a substantively identical letter asserting that it may be a PRP at the Site and similarly responsible for the cleanup of certain portions of the site. The general notice letters identify one other PRP at the site, and do not require specific action by Washington Mining or the Company at this time. At this juncture, the Company is unable to determine the likelihood of a materially adverse outcome or the amount or range of a potential loss with respect to any remedial action related to the Bonita Peak Mining District NPL site.
Operating Properties
Mueller Copper Tube Products, Inc.
In 1999, Mueller Copper Tube Products, Inc. (MCTP), a wholly owned subsidiary, commenced a cleanup and remediation of soil and groundwater at its Wynne, Arkansas plant to remove trichloroethylene, a cleaning solvent formerly used by MCTP. On August 30, 2000, MCTP received approval of its Final Comprehensive Investigation Report and Storm Water Drainage Investigation Report addressing the treatment of soils and groundwater from the Arkansas Department of Environmental Quality (ADEQ). The Company established a reserve for this project in connection with the acquisition of MCTP in 1998. Effective November 17, 2008, MCTP entered into a Settlement Agreement and Administrative Order by Consent to submit a Supplemental Investigation Work Plan (SIWP) and subsequent Final Remediation Work Plan (RWP) for the site. By letter dated January 20, 2010, ADEQ approved the SIWP as submitted, with changes acceptable to the Company. On December 16, 2011, MCTP entered into an amended Administrative Order by Consent to prepare and implement a revised RWP regarding final remediation for the Site. The remediation system was activated in February 2014. Costs to implement the work plans, including associated general and administrative costs, are estimated to approximate $0.8 million to $1.2 million over the next eight years.
United States Department of Commerce Antidumping Review
On December 24, 2008, the Department of Commerce (DOC) initiated an antidumping administrative review of the antidumping duty order covering circular welded non-alloy steel pipe and tube from Mexico for the November 1, 2007 through October 31, 2008 period of review. The DOC selected Mueller Comercial as a respondent in the review. On April 19, 2010, the DOC published the final results of the review and assigned Mueller Comercial an antidumping duty rate of 48.33 percent. On May 25, 2010, the Company appealed the final results to the U.S. Court of International Trade (CIT). On December 16, 2011, the CIT issued a decision remanding the Department’s final results. While the matter was still pending, the Company and the United States reached an agreement to settle the appeal. Subject to the conditions of the agreement, the Company anticipated that certain of its subsidiaries would incur antidumping duties on subject imports made during the period of review and, as such, established a reserve for this matter. After the lapse of the statutory period of time during which U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) was required, but failed, to liquidate the entries at the settled rate, the Company released the reserve. Between October 30, 2015 and November 27, 2015, CBP sent a series of invoices to Southland Pipe Nipples Co., Inc. (Southland), requesting payment of approximately $3.0 million in duties and interest in connection with 795 import entries made during the November 1, 2007 through October 31, 2008 period. On January 26, 2016 and January 27, 2016, Southland filed protests with CBP in connection with these invoices, noting that CBP’s asserted claims were not made in accordance with applicable law, including statutory provisions governing deemed liquidation. The Company believes in the merits of the legal objections raised in Southland’s protests, and CBP’s response to Southland’s protests is currently pending. Given the procedural posture and issues raised by this legal dispute, the Company cannot estimate the amount of potential duty liability, if any, that may result from CBP’s asserted claims.
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission Matter
On October 5, 2016, the Company received a demand letter from the Los Angeles District Office of the United States Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The EEOC alleged that between May 2011 and April 2015, various Company employees were terminated in violation of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), and that certain of the Company’s employee leave and attendance policies were discriminatory in nature. Thereafter, the Company, in consultation with its liability insurers, entered into conciliation and mediation efforts with the EEOC for purposes of resolving the claims. At the conclusion of those efforts, the Company and the EEOC reached agreement on a consensual resolution of the EEOC’s claims, which includes both monetary and equitable relief.
On June 28, 2018, the EEOC filed a complaint against the Company on behalf of a group of unidentified claimants in the United States District Court for the Central District of California alleging that the Company engaged in unlawful employment practices in violation of the ADA. On July 13, 2018, the District Court approved a Consent Decree between the Company and the EEOC to resolve the EEOC’s claims. The Consent Decree, the term of which shall be two and a half years, provides that the Company shall pay up to $1.0 million in monetary relief to fund individual claims for discrimination under the ADA as approved by the EEOC. That amount is fully within the limits of the Company’s applicable insurance coverage. Pursuant to the Consent Decree, the Company shall also take a series of proactive measures to cultivate a work environment free from unlawful discrimination. Those measures include, among others, assistance with the identification of potential claimants, employee, supervisory and managerial training regarding employee rights under the ADA, revised practices and procedures concerning reasonable workplace accommodations as required by the ADA, and related reporting and recordkeeping.
Guarantees
Guarantees, in the form of letters of credit, are issued by the Company generally to assure the payment of insurance deductibles and certain retiree health benefits. The terms of the guarantees are generally one year but are renewable annually as required. These letters are primarily backed by the Company’s revolving credit facility. The maximum payments that the Company could be required to make under its guarantees at September 29, 2018 were $8.5 million.
Note 10 – Income Taxes
The Company’s effective tax rate for the third quarter of 2018 was 12 percent compared with 27 percent for the same period last year. The items impacting the effective tax rate for the third quarter of 2018 were primarily attributable to a reduction of $4.3 million, or seven cents per diluted share, related to the provisional transition tax calculation and the reduction for the impact of investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $0.7 million. These were partially offset by the provision for state income taxes, net of the federal benefit, of $0.7 million and an increase in valuation allowance of $1.5 million, or three cents per diluted share.
The Company’s effective tax rate for the third quarter of 2017 was 27 percent. The items impacting the effective tax rate for the third quarter of 2017 were primarily attributable to reductions for the U.S. production activities deduction of $0.6 million, the effect of foreign tax rates lower than statutory tax rates of $1.6 million, and the tax benefit of equity compensation deductions of $0.5 million.
The Company’s effective tax rate for the first nine months of 2018 was 20 percent compared with 29 percent for the same period last year. The items impacting the effective tax rate for the first nine months of 2018 were primarily attributable to a reduction of $4.3 million, or seven cents per diluted share, related to the provisional transition tax calculation and a reduction for the impact of investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $4.4 million. These were partially offset by the provision for state income taxes, net of the federal benefit, of $3.3 million, an increase in valuation allowance of $1.5 million, or three cents per diluted share, the effect of foreign tax rates different than statutory rates of $0.8 million, and the inclusion for global intangible low-taxed income (GILTI) of $0.8 million.
The Company records the U.S. tax effects of its investment in Tecumseh, an unconsolidated affiliate, in income tax expense in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income.
The Company’s effective tax rate for the first nine months of 2017 was 29 percent. The items impacting the effective tax rate for the first nine months of 2017 were primarily attributable to reductions for the U.S. production activities deduction of $2.4 million, the effect of foreign tax rates lower than statutory tax rates of $4.6 million, the tax benefit of equity compensation deductions of $2.2 million, and the impact of investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $0.9 million. These items were partially offset by the provision for state income taxes, net of the federal benefit, of $1.7 million.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the Act) was enacted on December 22, 2017. The Act reduces the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent, requires companies to pay a one-time transition tax on the accumulated earnings of certain foreign subsidiaries, and creates new taxes on certain foreign-sourced earnings. The Company is applying the guidance in SAB 118 in accounting for the enactment date effects of the Act. At December 30, 2017, the Company made a reasonable estimate of the one-time transition tax on accumulated foreign earnings as well as the impact of the Act on its existing deferred tax balances. As discussed below, the Company has not completed its accounting for the tax effects of the Act as of September 29, 2018.
The one-time transition tax is based on the Company’s total post-1986 earnings and profits (E&P) for which the accrual of U.S. income taxes had previously been deferred. The Company recorded a provisional amount for its one-time transition tax liability of $12.9 million at December 30, 2017, and adjusted this amount to $8.6 million during the third quarter of 2018. The Company continues to refine its calculation of the total post-1986 foreign E&P for these foreign subsidiaries. Further, on August 1, 2018, the Treasury Department issued proposed regulations related to the calculation of the transition tax, and the Company is analyzing the impact of these regulations on the calculation of the transition tax. Accordingly, the Company’s estimate of the one-time transition tax may change when it finalizes the calculation of post-1986 foreign E&P previously deferred from U.S. federal taxation and finalizes its analysis of the regulations.
At December 30, 2017, the Company remeasured certain deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future, which is generally 21 percent. A provisional tax benefit of $12.1 million was recorded, and no adjustment was recorded to this estimate in the current quarter. The Company is still analyzing certain aspects of the Act and refining its calculations, which could potentially affect the measurement of these balances.
The GILTI provisions of the Act impose a tax on the GILTI earned by certain foreign subsidiaries. The FASB Staff Q&A, Topic 740, No. 5, Accounting for Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income, states that an entity can make an accounting policy election to either recognize deferred taxes for temporary basis differences expected to reverse as GILTI in future years or provide for the tax expense related to GILTI in the year the tax is incurred. Given the complexity of the GILTI provisions, the Company is still evaluating the effects of these provisions and has not yet determined the new accounting policy. At September 29, 2018, because the Company is still assessing the GILTI provisions and future income subject to the GILTI provisions, it has included an estimate of the tax on GILTI related to current-year operations in the forecasted effective tax rate and has not provided additional GILTI on deferred items.
The Company files a consolidated U.S. federal income tax return and numerous consolidated and separate-company income tax returns in many state, local, and foreign jurisdictions. The statute of limitations is open for the Company’s federal tax return and most state income tax returns for 2015 and all subsequent years and is open for certain state and foreign returns for earlier tax years due to ongoing audits and differing statute periods. While the Company believes that it is adequately reserved for possible future audit adjustments, the final resolution of these examinations cannot be determined with certainty and could result in final settlements that differ from current estimates.
Note 11 – Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
AOCI includes certain foreign currency translation adjustments from those subsidiaries not using the U.S. dollar as their functional currency, net deferred gains and losses on certain derivative instruments accounted for as cash flow hedges, adjustments to pension and OPEB liabilities, unrealized gains and losses on marketable securities classified as available-for-sale, and other comprehensive income attributable to unconsolidated affiliates.
The following tables provide changes in AOCI by component, net of taxes and noncontrolling interests (amounts in parentheses indicate debits to AOCI):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 29, 2018 |
(In thousands) | | Cumulative Translation Adjustment | | Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Derivatives | | Pension/OPEB Liability Adjustment | | Unrealized Gain on Equity Securities | | Attributable to Unconsol. Affiliates | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as of December 30, 2017 | | $ | (38,163 | ) | | $ | 847 |
| | $ | (20,610 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | 6,870 |
| | $ | (51,056 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive (loss) income before reclassifications | | (5,143 | ) | | (441 | ) | | 551 |
| | — |
| | (7,187 | ) | | (12,220 | ) |
Amounts reclassified from AOCI | | — |
| | (455 | ) | | 218 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (237 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net current-period other comprehensive (loss) income | | (5,143 | ) | | (896 | ) | | 769 |
| | — |
| | (7,187 | ) | | (12,457 | ) |
Reclassification of stranded effects of the Act | | — |
| | 112 |
| | (1,018 | ) | | — |
| | 1,462 |
| | 556 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as of September 29, 2018 | | $ | (43,306 | ) | | $ | 63 |
| | $ | (20,859 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | 1,145 |
| | $ | (62,957 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 |
(In thousands) | | Cumulative Translation Adjustment | | Unrealized (Loss) Gain on Derivatives | | Pension/OPEB Liability Adjustment | | Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities | | Attributable to Unconsol. Affiliates | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as of December 31, 2016 | | $ | (49,965 | ) | | $ | (300 | ) | | $ | (23,046 | ) | | $ | 380 |
| | $ | 5,975 |
| | $ | (66,956 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | 18,209 |
| | (1,175 | ) | | (1,309 | ) | | (1 | ) | | (1,086 | ) | | 14,638 |
|
Amounts reclassified from AOCI | | (3,777 | ) | | 1,360 |
| | 737 |
| | (379 | ) | | — |
| | (2,059 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net current-period other comprehensive income (loss) | | 14,432 |
| | 185 |
| | (572 | ) | | (380 | ) | | (1,086 | ) | | 12,579 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as of September 30, 2017 | | $ | (35,533 | ) | | $ | (115 | ) | | $ | (23,618 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | 4,889 |
| | $ | (54,377 | ) |
Reclassification adjustments out of AOCI were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Amount reclassified from AOCI |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended | | |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | Affected line item |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Unrealized losses (gains) on derivatives: | | | | | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts | | $ | (204 | ) | | $ | 223 |
| | $ | (550 | ) | | $ | 1,247 |
| | Cost of goods sold |
Interest rate swap | | — |
| | 232 |
| | — |
| | 696 |
| | Interest expense |
| | 24 |
| | (69 | ) | | 95 |
| | (583 | ) | | Income tax expense (benefit) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | (180 | ) | | $ | 386 |
| | $ | (455 | ) | | $ | 1,360 |
| | Net of tax and noncontrolling interests |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Amortization of net loss and prior service cost on employee benefit plans | | $ | 81 |
| | $ | 301 |
| | $ | 243 |
| | $ | 902 |
| | Other income, net |
| | (9 | ) | | (55 | ) | | (25 | ) | | (165 | ) | | Income tax benefit |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 72 |
| | $ | 246 |
| | $ | 218 |
| | $ | 737 |
| | Net of tax and noncontrolling interests |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Sale of available-for-sale securities | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | (611 | ) | | Other income, net |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 232 |
| | Income tax expense |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | (379 | ) | | Net of tax and noncontrolling interests |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Gain recognized upon sale of business | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | (3,777 | ) | | Gain on sale of assets |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | Income tax expense |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | (3,777 | ) | | Net of tax and noncontrolling interests |
Note 12 – Noncontrolling Interests
|
| | | |
(In thousands) | Noncontrolling Interests |
| |
Balance as of December 30, 2017 | $ | 13,917 |
|
Dividends paid to noncontrolling interests | (592 | ) |
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1,487 |
|
Other comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests, net of tax: | |
Foreign currency translation | (390 | ) |
| |
|
Balance as of September 29, 2018 | $ | 14,422 |
|
Item 2. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
General Overview
We are a leading manufacturer of copper, brass, aluminum, and plastic products. The range of these products is broad: copper tube and fittings; line sets; brass and copper alloy rod, bar, and shapes; aluminum and brass forgings; aluminum impact extrusions; PEX plastic tube, refrigeration valves and fittings; fabricated tubular products; and steel nipples. We also resell brass and plastic plumbing valves, plastic fittings, malleable iron fittings, faucets, and plumbing specialty products. Mueller’s operations are located throughout the United States and in Canada, Mexico, Great Britain, South Korea, and China.
Each of our reportable segments is composed of certain operating segments that are aggregated primarily by the nature of products offered as follows:
| |
• | Piping Systems: The Piping Systems segment is composed of Domestic Piping Systems Group, Great Lakes Copper, Heatlink Group, Die-Mold, European Operations, Trading Group, and Jungwoo-Mueller (our South Korean joint venture). The Domestic Piping Systems Group manufactures copper tube, fittings, and line sets. These products are manufactured in the U.S., sold in the U.S., and exported to markets worldwide. Great Lakes Copper manufactures copper tube and line sets in Canada and sells the products primarily in the U.S. and Canada. Heatlink Group manufactures a complete line of products for PEX plumbing and radiant systems in Canada and sells these products in Canada and the U.S. Die-Mold manufactures PEX and other plumbing-related fittings and plastic injection tooling in Canada and sells these products in Canada and the U.S. European Operations manufacture copper tube in the United Kingdom, which is sold throughout Europe. The Trading Group manufactures pipe nipples and sources products for import distribution in North America. Jungwoo-Mueller manufactures copper-based joining products that are sold worldwide. The Piping Systems segment sells products to wholesalers in the plumbing and refrigeration markets, distributors to the manufactured housing and recreational vehicle industries, building material retailers, and air-conditioning original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). |
The Company disposed of Mueller-Xingrong (the Company’s Chinese joint venture) on June 21, 2017. This business manufactured engineered copper tube primarily for air-conditioning applications in China.
| |
• | Industrial Metals: The Industrial Metals segment is composed of Brass Rod & Copper Bar Products, Impacts & Micro Gauge, and Brass Value-Added Products. The segment manufactures and sells brass and copper alloy rod, bar, and shapes; aluminum and brass forgings; aluminum impact extrusions; and gas valves and assemblies. The segment manufactures and sells its products primarily to domestic OEMs in the industrial, transportation, construction, heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning, plumbing, refrigeration, and energy markets. |
| |
• | Climate: The Climate segment is composed of Refrigeration Products, Fabricated Tube Products, Westermeyer, Turbotec, and ATCO. The segment manufactures and sells refrigeration valves and fittings, fabricated tubular products, high pressure components, coaxial heat exchangers, and insulated HVAC flexible duct systems. The segment sells its products primarily to the heating, ventilation, air-conditioning, and refrigeration markets in the U.S. |
New housing starts and commercial construction are important determinants of our sales to the heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning, refrigeration, and plumbing markets because the principal end use of a significant portion of our products is in the construction of single and multi-family housing and commercial buildings. Repairs and remodeling projects are also important drivers of underlying demand for these products.
Residential construction activity has shown improvement in recent years, but remains at levels below long-term historical averages. Per the U.S. Census Bureau, the September 2018 seasonally adjusted annual rate of new housing starts was 1.2 million, which was consistent with the September 2017 rate. Mortgage rates remain at historically low levels, as the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate was 4.46 percent for the first nine months of 2018 and 3.99 percent for the twelve months ended December 2017. The private non-residential construction sector, which includes offices, industrial, health care, and retail projects, has shown improvement in recent years. Per the U.S. Census Bureau, the seasonally adjusted annual value of private nonresidential construction put in place was $452.9 billion in August 2018 compared to the August 2017 rate of $432.0 billion. We expect that most of these conditions will continue to improve.
Profitability of certain of our product lines depends upon the “spreads” between the costs of raw materials and the selling prices of our products. The open market prices for copper cathode and copper and brass scrap, for example, influence the selling price of copper tube and brass rod, two principal products manufactured by the Company. We attempt to minimize the effects on
profitability from fluctuations in material costs by passing through these costs to our customers. Our earnings and cash flow are dependent upon these spreads that fluctuate based upon market conditions.
Earnings and profitability are also impacted by unit volumes that are subject to market trends, such as substitute products, imports, technologies, and market share. In core product lines, we intensively manage our pricing structure while attempting to maximize profitability. From time-to-time, this practice results in lost sales opportunities and lower volume. For plumbing systems, plastics are the primary substitute product; these products represent an increasing share of consumption. U.S. consumption of copper tube is still predominantly supplied by U.S. manufacturers. For certain air-conditioning and refrigeration applications, aluminum-based systems are the primary substitution threat. We cannot predict the acceptance or the rate of switching that may occur. In recent years, brass rod consumption in the U.S. has declined due to the outsourcing of many manufactured products to offshore regions.
Results of Operations
Consolidated Results
The following table compares summary operating results for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | Percent Change | | For the Nine Months Ended | | Percent Change |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 645,958 |
| | $ | 550,363 |
| | 17.4 | % | | $ | 1,948,791 |
| | $ | 1,742,549 |
| | 11.8 | % |
Operating income | | 33,671 |
| | 37,481 |
| | (10.2 | ) | | 133,007 |
| | 129,737 |
| | 2.5 |
|
Net income | | 20,292 |
| | 22,258 |
| | (8.8 | ) | | 77,602 |
| | 79,878 |
| | (2.8 | ) |
The following are components of changes in net sales compared to the prior year:
|
| | | | | | |
| | Quarter-to-
Date | | Year-to-
Date |
Net selling price in core product lines | | 1.8 | % | | 7.2 | % |
Unit sales volume in core product lines | | 7.2 |
| | 3.8 |
|
Acquisitions | | 8.8 |
| | 3.5 |
|
Dispositions | | — |
| | (3.9 | ) |
Other | | (0.4 | ) | | 1.2 |
|
| | | | |
| | 17.4 | % | | 11.8 | % |
The increase in net sales during the third quarter of 2018 was primarily due to (i) sales of $46.1 million recorded by ATCO, acquired in July 2018, (ii) higher unit sales volume of $39.5 million in our core product lines, primarily copper tube and brass rod, (iii) higher net selling prices of $9.6 million in our core product lines, and (iv) sales of $2.3 million recorded by Die-Mold, acquired in March 2018.
The increase in net sales during the first nine months of 2018 was primarily due to (i) higher net selling prices of $126.3 million in our core product lines, (ii) higher unit sales volume of $95.3 million in our domestic core product lines, (iii) sales of $46.1 million recorded by ATCO, (iv) an increase in sales in our non-core product lines of $20.8 million, (v) incremental sales of $9.7 million recorded by Heatlink Group, acquired in June 2017, and (vi) sales of $4.5 million recorded by Die-Mold. These increases were offset by (i) the absence of sales of $67.3 million recorded by Mueller-Xingrong and (ii) lower unit sales volume of $29.1 million in our non-domestic core product lines.
Net selling prices generally fluctuate with changes in raw material costs. Changes in raw material costs are generally passed through to customers by adjustments to selling prices. The following graph shows the Comex average copper price per pound by quarter for the current and prior fiscal years:
The following tables compare cost of goods sold and operating expenses as dollar amounts and as a percent of net sales for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 566,956 |
| | $ | 471,262 |
| | $ | 1,676,446 |
| | $ | 1,484,000 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 10,619 |
| | 8,266 |
| | 29,081 |
| | 25,216 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 38,889 |
| | 33,214 |
| | 112,077 |
| | 104,676 |
|
Asset impairments | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 411 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (2,691 | ) | | 140 |
| | (334 | ) | | (1,491 | ) |
Insurance recovery | | (1,486 | ) | | — |
| | (1,486 | ) | | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | $ | 612,287 |
| | $ | 512,882 |
| | $ | 1,815,784 |
| | $ | 1,612,812 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
| | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 87.8 | % | | 85.6 | % | | 86.0 | % | | 85.2 | % |
Depreciation and amortization | | 1.6 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 1.4 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 6.0 |
| | 6.1 |
| | 5.8 |
| | 6.1 |
|
Asset impairments | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (0.4 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (0.1 | ) |
Insurance recovery | | (0.2 | ) | | — |
| | (0.1 | ) | | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | 94.8 | % | | 93.2 | % | | 93.2 | % | | 92.6 | % |
Q3 2018 compared to Q3 2017
The increase in cost of goods sold was primarily due to the increase in sales volume related to businesses acquired and in our core product lines. Depreciation and amortization increased in the third quarter of 2018 primarily as a result of depreciation and amortization of the long-lived assets of businesses acquired, as well as several new long-lived assets being placed into service. Selling, general, and administrative expense increased in the third quarter of 2018 primarily as a result of (i) incremental expenses associated with ATCO and Die-Mold of $5.2 million and (ii) an increase in employment costs, including incentive compensation, of $1.8 million. These increases were partially offset by fees of $1.5 million received for services provided under certain third-party sales and distribution arrangements. In addition, during the third quarter of 2018 we recognized a gain of $2.7 million on the sale of real property and a gain of $1.5 million for a payment receivable on the property damage portion of our insurance claim related to the September 2017 fire at our brass rod mill in Port Huron, Michigan.
Interest expense increased for the third quarter of 2018 primarily as a result of increased borrowing costs associated with our unsecured $350.0 million revolving credit facility. For the third quarter of 2018, we had other income, net of $0.4 million, compared to other expense, net of $0.4 million for the third quarter of 2017. This is primarily due to higher net periodic benefit income for our benefit plans and lower environmental remediation costs in the third quarter of 2018.
Our effective tax rate for the third quarter of 2018 was 12 percent compared with 27 percent for the same period last year. The items impacting the effective tax rate for the third quarter of 2018 were primarily attributable to a reduction of $4.3 million related to the provisional transition tax calculation and a reduction for the impact of investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $0.7 million. These were partially offset by the provision for state income taxes, net of the federal benefit, of $0.7 million and an increase in valuation allowance of $1.5 million.
For the third quarter of 2017, the difference between the effective tax rate and the amount computed using the U.S. federal statutory rate was primarily attributable to reductions for the U.S. production activities deduction of $0.6 million, the effect of foreign tax rates lower than statutory tax rates of $1.6 million, and the tax benefit of equity compensation deductions of $0.5 million.
During the third quarter of 2018 and the third quarter of 2017, we recognized losses of $3.1 million and $0.4 million, respectively, on our investments in unconsolidated affiliates.
YTD 2018 compared to YTD 2017
The increase in cost of goods sold was primarily due to the increase in the average cost of copper, our principal raw material, and the increase in sales volume in our domestic product lines and related to businesses acquired, partially offset by the decrease in sales volume resulting from the sale of Mueller-Xingrong. Depreciation and amortization increased in the first nine months of 2018 as a result of several new long-lived assets being placed into service as well as long-lived assets of businesses acquired, partially offset by the impact of the sale of long-lived assets at Mueller-Xingrong. Selling, general, and administrative expense increased for the first nine months of 2018 primarily as a result of (i) incremental expenses associated with ATCO, Heatlink Group, and Die-Mold of $7.7 million and (ii) an increase in employment costs, including incentive compensation, of $3.2 million. These increases were partially offset by (i) fees of $1.5 million received for services provided under certain third-party sales and distribution arrangements, (ii) the absence of expenses associated with Mueller-Xingrong of $1.2 million, and (iii) a reduction in product liability expense of $1.0 million. In addition, during the first nine months of 2018 we recognized a gain of $2.7 million on the sale of real property and a gain of $0.7 million on the sale of manufacturing equipment, which were offset by a loss of $3.1 million on the sale of a corporate aircraft. We also recognized a gain of $1.5 million for a payment receivable on the property damage portion of our insurance claim related to the September 2017 fire at our brass rod mill in Port Huron, Michigan during the first nine months of 2018. During the first nine months of 2017, we recognized a gain of $1.5 million on the sale of Mueller-Xingrong and fixed asset impairment charges for certain manufacturing equipment of $0.4 million.
Interest expense increased in the first nine months of 2018 primarily as a result of interest associated with our 6% Subordinated Debentures that were issued during the first quarter of 2017 as part of our special dividend, as well as increased borrowing costs associated with our unsecured $350.0 million revolving credit facility. Other income, net, for the first nine months of 2018 increased primarily as a result of higher net periodic benefit income for our benefit plans.
Our effective tax rate for the first nine months of 2018 was 20 percent compared with 29 percent for the same period last year. The items impacting the effective tax rate for the first nine months of 2018 were primarily attributable to a reduction of $4.3 million related to the provisional transition tax calculation and a reduction for the impact of investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $4.4 million. These were partially offset by the provision for state income taxes, net of the federal benefit, of $3.3 million, an increase in valuation allowance of $1.5 million, the effect of foreign tax rates different than statutory rates of $0.8 million, and the inclusion for global intangible low-taxed income of $0.8 million.
For the first nine months of 2017, the difference between the effective tax rate and the amount computed using the U.S. federal statutory rate was primarily attributable to reductions for the U.S. production activities deduction of $2.4 million, the effect of foreign tax rates lower than statutory tax rates of $4.6 million, the tax benefit of equity compensation deductions of $2.2 million, and the impact of investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $0.9 million. These items were partially offset by the provision for state income taxes, net of the federal benefit, of $1.7 million.
During the first nine months of 2018, we recognized losses of $13.6 million on our investments in unconsolidated affiliates. During the first nine months of 2017, we recognized $1.7 million of losses on these investments.
Piping Systems Segment
The following table compares summary operating results for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017 for the businesses comprising our Piping Systems segment:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | Percent Change | | For the Nine Months Ended | | Percent Change |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 410,525 |
| | $ | 384,078 |
| | 6.9 | % | | $ | 1,294,672 |
| | $ | 1,205,697 |
| | 7.4 | % |
Operating income | | 25,408 |
| | 20,941 |
| | 21.3 |
| | 100,376 |
| | 86,323 |
| | 16.3 |
|
The following are components of changes in net sales compared to the prior year:
|
| | | | | | |
| | Quarter-to-
Date | | Year-to-
Date |
Net selling price in core product lines | | 2.2 | % | | 7.2 | % |
Unit sales volume in core product lines | | 7.1 |
| | 3.3 |
|
Acquisitions | | 0.6 |
| | 1.2 |
|
Dispositions | | — |
| | (5.6 | ) |
Other | | (3.0 | ) | | 1.3 |
|
| | | | |
| | 6.9 | % | | 7.4 | % |
The increase in net sales during the third quarter of 2018 was primarily attributable to (i) higher unit sales volume of $26.6 million in the segment’s core product lines, primarily copper tube, (ii) higher net selling prices in the segment’s core product lines of $8.2 million, and (iii) sales of $2.3 million recorded by Die-Mold. These increases were offset by lower sales of $4.0 million in the segment’s non-core product lines.
Net sales during the first nine months of 2018 increased primarily as a result of (i) higher net selling prices in the segment’s core product lines of $87.1 million, (ii) higher unit sales volume of $69.2 million in the segment’s domestic core product lines, (iii) an increase in net sales of $12.7 million in the segment’s non-core product lines, (iv) incremental sales of $9.7 million recorded by Heatlink Group, and (v) sales of $4.5 million recorded by Die-Mold. These increases were offset by (i) the absence of sales of $67.3 million recorded by Mueller-Xingrong and (ii) lower unit sales volume of $29.1 million in the segment’s non-domestic core product lines.
The following tables compare cost of goods sold and operating expenses as dollar amounts and as a percent of net sales for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 363,174 |
| | $ | 340,191 |
| | $ | 1,120,890 |
| | $ | 1,049,098 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 5,946 |
| | 5,290 |
| | 17,568 |
| | 16,223 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 17,387 |
| | 17,516 |
| | 57,931 |
| | 55,133 |
|
Asset impairments | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 411 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (1,390 | ) | | 140 |
| | (2,093 | ) | | (1,491 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | $ | 385,117 |
| | $ | 363,137 |
| | $ | 1,194,296 |
| | $ | 1,119,374 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
| | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 88.5 | % | | 88.6 | % | | 86.6 | % | | 87.0 | % |
Depreciation and amortization | | 1.4 |
| | 1.4 |
| | 1.4 |
| | 1.3 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 4.2 |
| | 4.5 |
| | 4.4 |
| | 4.6 |
|
Asset impairments | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (0.3 | ) | | — |
| | (0.2 | ) | | (0.1 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | 93.8 | % | | 94.5 | % | | 92.2 | % | | 92.8 | % |
The increase in cost of goods sold during the third quarter of 2018 was primarily due to the increase in sales volume in the segment’s core product lines. Depreciation and amortization increased slightly primarily as a result of several new long-lived assets being placed into service as well as depreciation and amortization of the long-lived assets acquired at Die-Mold. Selling, general, and administrative expense decreased slightly for the third quarter of 2018 primarily as a result of fees of $1.5 million received for services provided under certain third-party sales and distribution arrangements. This decrease was largely offset by (i) an increase in employment costs, including incentive compensation, of $0.5 million, (ii) an increase in legal and professional fees of $0.4 million, and (iii) incremental expenses associated with Die-Mold of $0.2 million. In addition, we recognized a gain of $1.4 million on the sale of real property during the third quarter of 2018.
The increase in cost of goods sold during the first nine months of 2018 was primarily due to the increase in the average cost of copper and the increase in sales volume in the segment’s core product lines and related to the acquisitions of Heatlink Group and Die-Mold, partially offset by the decrease in sales volume resulting from the sale of Mueller-Xingrong. Depreciation and amortization increased slightly as a result of several new long-lived assets being placed into service as well as long-lived assets of Heatlink Group and Die-Mold, partially offset by the impact of the sale of long-lived assets at Mueller-Xingrong. Selling, general, and administrative expenses increased for the first nine months of 2018, primarily due to (i) incremental expenses associated with Die-Mold and Heatlink Group of $2.7 million, (ii) an increase in legal and professional fees of $1.6 million, and (iii) an increase in employment costs, including incentive compensation, of $0.6 million. These increases were partially offset by (i) fees of $1.5 million received for services provided under certain third-party sales and distribution arrangements and (ii) the absence of expenses associated with Mueller-Xingrong of $1.2 million. In addition, during the first nine months of 2018 we recognized a gain of $1.4 million on the sale of real property and a gain of $0.7 million on the sale of manufacturing equipment. During first nine months of 2017, we recognized a gain of $1.5 million on the sale of Mueller-Xingrong.
Industrial Metals Segment
The following table compares summary operating results for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017 for the businesses comprising our Industrial Metals segment:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | Percent Change | | For the Nine Months Ended | | Percent Change |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 158,709 |
| | $ | 147,578 |
| | 7.5 | % | | $ | 511,932 |
| | $ | 451,919 |
| | 13.3 | % |
Operating income | | 15,111 |
| | 22,698 |
| | (33.4 | ) | | 53,837 |
| | 59,434 |
| | (9.4 | ) |
The following are components of changes in net sales compared to the prior year:
|
| | | | | | |
| | Quarter-to-
Date | | Year-to-
Date |
Net selling price in core product lines | | 1.0 | % | | 8.9 | % |
Unit sales volume in core product lines | | 9.1 |
| | 6.0 |
|
Other | | (2.6 | ) | | (1.6 | ) |
| | | | |
| | 7.5 | % | | 13.3 | % |
The increase in net sales during the third quarter of 2018 was primarily due to (i) higher unit sales volume of $12.9 million in the segment’s core product lines, primarily brass rod, and (ii) higher net selling prices of $1.5 million.
The increase in net sales during the first nine months of 2018 was primarily due to (i) higher net selling prices of $39.1 million and (ii) higher unit sales volume of $26.1 million in the segment’s core product lines.
The following tables compare cost of goods sold and operating expenses as dollar amounts and as a percent of net sales for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 141,435 |
| | $ | 120,021 |
| | $ | 445,259 |
| | $ | 377,036 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 1,864 |
| | 1,845 |
| | 5,715 |
| | 5,647 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 3,086 |
| | 3,014 |
| | 9,908 |
| | 9,802 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (1,301 | ) | | — |
| | (1,301 | ) | | — |
|
Insurance recovery | | (1,486 | ) | | — |
| | (1,486 | ) | | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | $ | 143,598 |
| | $ | 124,880 |
| | $ | 458,095 |
| | $ | 392,485 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
| | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 89.1 | % | | 81.3 | % | | 87.0 | % | | 83.4 | % |
Depreciation and amortization | | 1.2 |
| | 1.3 |
| | 1.1 |
| | 1.2 |
|
Selling, general, and administrative expense | | 1.9 |
| | 2.0 |
| | 2.0 |
| | 2.2 |
|
(Gain) loss on sale of assets | | (0.8 | ) | | — |
| | (0.3 | ) | | — |
|
Insurance recovery | | (0.9 | ) | | — |
| | (0.3 | ) | | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | 90.5 | % | | 84.6 | % | | 89.5 | % | | 86.8 | % |
The increase in cost of goods sold during the third quarter of 2018 was primarily due to the increase in sales volume in the segment’s core product lines. Depreciation and amortization and selling, general, and administrative expenses for the third quarter of 2018 were consistent with what was recorded in the third quarter of 2017. In addition, during the third quarter of 2018 we recognized a gain of $1.3 million on the sale of real property and a gain of $1.5 million for a payment receivable on the property damage portion of our insurance claim related to the September 2017 fire at our brass rod mill in Port Huron, Michigan.
The increase in cost of goods sold during the first nine months of 2018 was primarily due to the increase in the average cost of copper and the increase in sales volume in the segment’s core product lines. Depreciation and amortization and selling, general, and administrative expenses for the first nine months of 2018 were consistent with what was recorded in the first nine months of 2017. In addition, during the first nine months of 2018 we recognized a gain of $1.3 million on the sale of real property and a gain of $1.5 million for a payment receivable on the property damage portion of our insurance claim related to the September 2017 fire at our brass rod mill in Port Huron, Michigan.
Climate Segment
The following table compares summary operating results for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 and 2017 for the businesses comprising our Climate segment:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | Percent Change | | For the Nine Months Ended | | Percent Change |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | 2018 vs. 2017 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 81,619 |
| | $ | 32,488 |
| | 151.2 | % | | $ | 156,854 |
| | $ | 103,403 |
| | 51.7 | % |
Operating income | | 5,774 |
| | 5,429 |
| | 6.4 |
| | 16,668 |
| | 17,155 |
| | (2.8 | ) |
Sales for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 increased primarily as a result of (i) sales of $46.1 million recorded by ATCO, (ii) an increase in volume, and (iii) change in product mix.
The following tables compare cost of goods sold and operating expenses as dollar amounts and as a percent of net sales for the first nine months of 2018 and 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
(In thousands) | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 66,832 |
| | $ | 24,111 |
| | $ | 124,806 |
| | $ | 77,124 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | | 2,123 |
| | 636 |
| | 3,371 |
| | 1,880 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expense | | 6,890 |
| | 2,312 |
| | 12,009 |
| | 7,244 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | $ | 75,845 |
| | $ | 27,059 |
| | $ | 140,186 |
| | $ | 86,248 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | | For the Nine Months Ended |
| | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 | | September 29, 2018 | | September 30, 2017 |
| | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | 81.9 | % | | 74.2 | % | | 79.6 | % | | 74.6 | % |
Depreciation and amortization | | 2.6 |
| | 2.0 |
| | 2.1 |
| | 1.8 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expense | | 8.4 |
| | 7.1 |
| | 7.7 |
| | 7.0 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Operating expenses | | 92.9 | % | | 83.3 | % | | 89.4 | % | | 83.4 | % |
Cost of goods sold increased during the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 primarily due to the increase in volume and change in product mix within the segment primarily resulting from the ATCO acquisition. In addition, it included additional expense of $2.2 million to adjust ATCO’s inventory to fair value as part of purchase accounting during 2018. Depreciation and amortization increased in the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 primarily as a result of depreciation and amortization of the long-lived assets acquired at ATCO. Selling, general, and administrative expenses for the third quarter and first nine months of 2018 increased as a result of incremental expenses associated with ATCO.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The following table presents selected financial information for the first nine months of 2018 and 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | |
(In thousands) | | 2018 | | 2017 |
| | | | |
Increase (decrease) in: | | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | | $ | (17,514 | ) | | $ | (250,162 | ) |
Property, plant, and equipment, net | | 56,334 |
| | (11,386 | ) |
Total debt | | 54,214 |
| | 175,904 |
|
Working capital, net of cash and current debt | | 28,366 |
| | 18,106 |
|
| | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 122,515 |
| | 53,542 |
|
Net cash used in investing activities | | (166,278 | ) | | (8,008 | ) |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | 26,691 |
| | (300,162 | ) |
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
During the nine months ended September 29, 2018, net cash provided by operating activities was primarily attributable to (i) consolidated net income of $79.1 million, (ii) a decrease in inventories of $48.7 million, (iii) depreciation and amortization of $29.3 million, (iv) losses from unconsolidated affiliates of $13.6 million, and (v) a decrease in other assets of $11.3 million. This cash increase was offset by (i) an increase in accounts receivable of $42.2 million, (ii) a decrease in other liabilities of $13.9 million, and (iii) a decrease in current liabilities of $7.9 million. The decrease in inventories was primarily driven by the use of excess inventory built at the end of 2017 due to a casting outage in our brass rod mill that impaired our ability to melt scrap returns. The fluctuations in accounts receivable and current liabilities were primarily due to increased selling prices and sales volume in certain businesses and additional working capital needs in the first nine months of 2018. The changes in other assets and liabilities are primarily attributable to the change in estimate of the one-time transition tax liability on accumulated foreign earnings under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, net cash provided by operating activities was primarily attributable to (i) consolidated net income of $81.0 million, (ii) depreciation and amortization of $25.4 million, and (iii) an increase in current liabilities of $21.0 million. This cash increase was offset by (i) an increase in accounts receivables of $33.4 million and (ii) an increase in inventories of $40.9 million. The fluctuations were primarily due to increased sales volume in certain businesses and additional working capital needs in the first nine months of 2017.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
The major components of net cash used in investing activities during the nine months ended September 29, 2018 included (i) $167.7 million for the purchases of ATCO and Die-Mold, net of cash acquired, and (ii) capital expenditures of $16.7 million. These uses of cash were offset by proceeds on the sale of properties of $18.7 million.
The major components of net cash used in investing activities during the nine months ended September 30, 2017 included (i) $18.4 million for the purchase of Heatlink Group, net of cash acquired, (ii) capital expenditures of $17.3 million, and (iii) investments in our joint venture in Bahrain of $3.3 million. These uses of cash were offset by (i) $17.5 million of proceeds from the sale of our 50.5 percent equity interest in Mueller-Xingrong, net of cash sold, (ii) proceeds from the sale of properties of $11.7 million, and (iii) proceeds from the sale of securities of $1.8 million.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
For the nine months ended September 29, 2018, net cash provided by financing activities consisted primarily of the issuance of debt under our Credit Agreement of $190.0 million. This was offset by (i) $135.0 million used to reduce the debt outstanding under our Credit Agreement, (ii) $17.1 million used for the payment of regular quarterly dividends to stockholders of the Company, (iii) $6.6 million used to repurchase common stock, and (iv) $3.0 million used for repayment of debt by Jungwoo-Mueller.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2017, net cash used in financing activities consisted primarily of (i) $191.2 million used for payment of the special dividend and regular quarterly dividends to stockholders of the Company, (ii) $100.0 million used to reduce the debt outstanding under our Credit Agreement, (iii) $3.5 million used for repayment of debt by Mueller-Xingrong and Jungwoo-Mueller, and (iv) $2.9 million used for payment of dividends to noncontrolling interests.
Liquidity and Outlook
We believe that cash provided by operations, funds available under the Credit Agreement, and cash on hand will be adequate to meet our liquidity needs, including working capital, capital expenditures, and debt payment obligations. As of September 29, 2018 our current ratio was 3.1 to 1.
We have significant environmental remediation obligations which we expect to pay over future years. Cash used for environmental remediation activities was approximately $4.6 million during the first nine months of 2018. We expect to spend approximately $0.9 million for the remainder of 2018 for ongoing environmental remediation activities.
The Company declared and paid a quarterly cash dividend of 10.0 cents per common share during the first, second, and third quarters of 2018 and 2017. Additionally, during the first quarter of 2017, the Company distributed a special dividend composed of $3.00 in cash and $5.00 in principal amount of the Company’s 6% Subordinated Debentures (Debentures) due 2027 for each share of common stock outstanding. Payment of dividends in the future is dependent upon our financial condition, cash flows, capital requirements, earnings, and other factors.
Long-Term Debt
As of September 29, 2018, the Company’s total debt was $519.3 million or 47.1 percent of its total capitalization.
The Debentures distributed as part of our special dividend are subordinated to all other funded debt of the Company and are callable, in whole or in part, at any time at the option of the Company, subject to declining call premiums during the first five years. The Debentures also grant each holder the right to require the Company to repurchase such holder’s Debentures in the event of a change in control at declining repurchase premiums during the first five years. Interest is payable semiannually on September 1 and March 1, and commenced September 1, 2017. Total Debentures outstanding as of September 29, 2018 were $284.5 million.
The Company’s Credit Agreement provides for an unsecured $350.0 million revolving credit facility which matures on December 6, 2021. Total borrowings under the Credit Agreement were $215.0 million at September 29, 2018. The Credit Agreement backed approximately $8.5 million in letters of credit at the end of the third quarter of 2018.
Covenants contained in the Company’s financing obligations require, among other things, the maintenance of minimum levels of tangible net worth and the satisfaction of certain minimum financial ratios. As of September 29, 2018, the Company was in compliance with all of its debt covenants.
Share Repurchase Program
The Board of Directors has extended, until August 2019, the authorization to repurchase up to 20 million shares of the Company’s common stock through open market transactions or through privately negotiated transactions. We may cancel, suspend, or extend the time period for the repurchase of shares at any time. Any repurchases will be funded primarily through existing cash and cash from operations. We may hold any shares repurchased in treasury or use a portion of the repurchased shares for our stock-based compensation plans, as well as for other corporate purposes. From its initial authorization in 1999 through September 29, 2018, the Company has repurchased approximately 5.0 million shares under this authorization.
In October 2018, the Company repurchased approximately 242 thousand shares under the authorization for a total of $6.2 million.
Contractual Cash Obligations
There have been no significant changes in our contractual cash obligations reported at December 30, 2017.
Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
The Company is exposed to market risk from changes in raw material and energy costs, interest rates, and foreign currency exchange rates. To reduce such risks, we may periodically use financial instruments. Hedging transactions are authorized and executed pursuant to policies and procedures. Further, we do not buy or sell financial instruments for trading purposes.
Cost and Availability of Raw Materials and Energy
Raw materials, primarily copper and brass, represent the largest component of the Company’s variable costs of production. The cost of these materials is subject to global market fluctuations caused by factors beyond our control. Significant increases in the cost of metal, to the extent not reflected in prices for our finished products, or the lack of availability could materially and adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
The Company occasionally enters into future fixed-price arrangements with certain customers. We may utilize futures contracts to hedge risks associated with these forward fixed-price arrangements. We may also utilize futures contracts to manage price risk associated with inventory. Depending on the nature of the hedge, changes in the fair value of the futures contracts will either be offset against the change in fair value of the inventory through earnings or recognized as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) in equity and reflected in earnings upon the sale of inventory. Periodic value fluctuations of the contracts generally offset the value fluctuations of the underlying fixed-price transactions or inventory. At September 29, 2018, we held open futures contracts to purchase approximately $66.0 million of copper over the next 15 months related to fixed-price sales orders and to sell approximately $4.5 million of copper over the next three months related to copper inventory.
We may enter into futures contracts or forward fixed-price arrangements with certain vendors to manage price risk associated with natural gas purchases. The effective portion of gains and losses with respect to these positions are deferred in equity as a component of AOCI and reflected in earnings upon consumption of natural gas. Periodic value fluctuations of the futures contracts generally offset the value fluctuations of the underlying natural gas prices. As of September 29, 2018, we held no open futures contracts to purchase natural gas.
Interest Rates
At September 29, 2018, we had variable-rate debt outstanding of $219.4 million. At this borrowing level, a hypothetical 10 percent increase in interest rates would have had an insignificant unfavorable impact on our pretax earnings and cash flows. The primary interest rate exposure on variable-rate debt is based on LIBOR.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
Foreign currency exposures arising from transactions include firm commitments and anticipated transactions denominated in a currency other than an entity’s functional currency. The Company and its subsidiaries generally enter into transactions denominated in their respective functional currencies. We may utilize certain futures or forward contracts with financial institutions to hedge foreign currency transactional exposures. Gains and losses with respect to these positions are deferred in equity as a component of AOCI and reflected in earnings upon collection of receivables or payment of commitments. At September 29, 2018, we had open forward contracts with a financial institution to sell approximately 5.1 million euros, 25.6 million Swedish kronor, and 8.3 million Norwegian kroner through January 2019.
The Company’s primary foreign currency exposure arises from foreign-denominated revenues and profits and their translation into U.S. dollars. The primary currencies to which we are exposed include the Canadian dollar, the British pound sterling, the euro, the Mexican peso, the South Korean won, and the Chinese renminbi. The Company generally views its investments in foreign subsidiaries with a functional currency other than the U.S. dollar as long-term. As a result, we generally do not hedge these net investments.
Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward Looking Information
This Quarterly Report contains various forward-looking statements and includes assumptions concerning the Company’s operations, future results, and prospects. These forward-looking statements are based on current expectations and are subject to risk and uncertainties, and may be influenced by factors that could cause actual outcomes and results to be materially different from those predicted. The forward-looking statements reflect knowledge and information available as of the date of preparation of the Quarterly Report, and the Company undertakes no obligation to update these forward-looking statements. We identify the forward-looking statements by using the words “anticipates,” “believes,” “expects,” “intends” or similar expressions in such statements.
In connection with the “safe harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, the Company provides the following cautionary statement identifying important economic, political, and technological factors, among others, which could cause actual results or events to differ materially from those set forth in or implied by the forward-looking statements and related assumptions. In addition to those factors discussed under “Risk Factors” in the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 30, 2017, such factors include: (i) the current and projected future business environment, including interest rates and capital and consumer spending; (ii) the domestic housing and commercial construction industry environment; (iii) availability and price fluctuations in commodities (including copper, natural gas, and other raw materials, including crude oil that indirectly affects plastic resins); (iv) competitive factors and competitor responses to the Company’s initiatives; (v) stability of government laws and regulations, including taxes; (vi) availability of financing; and (vii) continuation of the environment to make acquisitions, domestic and foreign, including regulatory requirements and market values of candidates.
Item 4. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains disclosure controls and procedures designed to ensure information required to be disclosed in Company reports filed under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed in Company reports filed under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures pursuant to Rule 13a-15(e) of the Exchange Act as of September 29, 2018. Based on that evaluation, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are effective as of September 29, 2018 to ensure that information required to be disclosed in Company reports filed under the Exchange Act is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC rules and forms and (ii) accumulated and communicated to management, including the Company’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting during the Company’s fiscal quarter ending September 29, 2018, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
PART II. OTHER INFORMATION
Item 1. Legal Proceedings
General
The Company is involved in certain litigation as a result of claims that arose in the ordinary course of business. Additionally, the Company may realize the benefit of certain legal claims and litigation in the future; these gain contingencies are not recognized in the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. For a description of material pending legal proceedings, see “Note 9 - Commitments and Contingencies” in the Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements, which is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
The Company is exposed to risk as it operates its businesses. To provide a framework to understand the operating environment of the Company, we have provided a brief explanation of the more significant risks associated with our businesses in our 2017 Annual Report on Form 10-K. There have been no material changes in risk factors that were previously disclosed in our 2017 Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 2. Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The Company’s Board of Directors has extended, until August 2019, the authorization to repurchase up to 20 million shares of the Company’s common stock through open market transactions or through privately negotiated transactions. The Company may cancel, suspend, or extend the time period for the repurchase of shares at any time. Any repurchases will be funded primarily through existing cash and cash from operations. The Company may hold any shares repurchased in treasury or use a portion of the repurchased shares for its stock-based compensation plans, as well as for other corporate purposes. From its initial authorization in 1999 through September 29, 2018, the Company had repurchased approximately 5.0 million shares under this authorization. Below is a summary of the Company’s stock repurchases for the period ended September 29, 2018. In October 2018, the Company repurchased approximately 242 thousand shares under the authorization for a total of $6.2 million.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (a) Total Number of Shares Purchased (1) | | (b) Average Price Paid per Share | | (c) Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | | (d) Maximum Number of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (2) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
July 1, 2018 - July 28, 2018 | | 5,658 |
| | $ | 32.00 |
| | — |
| | 15,037,060 |
|
July 29, 2018 - August 25, 2018 | | 35,138 |
| | $ | 32.15 |
| | — |
| | 15,037,060 |
|
August 26, 2018 - September 29, 2018 | | 513 |
| | $ | 28.90 |
| | — |
| | 15,037,060 |
|
Total | | 41,309 |
| | | | — |
| | |
(1) Shares tendered to the Company by holders of stock-based awards in payment of the purchase price and/or withholding taxes upon exercise and/or vesting. Also includes shares resulting from restricted stock forfeitures at the average cost of treasury stock.
(2) Shares available to be purchased under the Company’s 20 million share repurchase authorization until August 2019. The extension of the authorization was announced on October 24, 2018.
Item 6. Exhibits
|
| |
10.1 | |
| |
10.2 | |
| |
31.1 | |
| |
31.2 | |
| |
32.1 | |
| |
32.2 | |
| |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase |
| |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase |
| |
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document |
| |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase |
| |
101.PRE | XBRL Presentation Linkbase Document |
| |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema |
Items 3, 4, and 5 are not applicable and have been omitted.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
|
| |
| MUELLER INDUSTRIES, INC. |
| |
| |
| /s/ Jeffrey A. Martin |
| Jeffrey A. Martin |
October 24, 2018 | Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
Date | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
| |
| |
| /s/ Anthony J. Steinriede |
October 24, 2018 | Anthony J. Steinriede |
Date | Vice President – Corporate Controller |
| |